Google SEO Comprehensive Guide

In today’s digital era of 2025, search engine traffic has become one of the key factors for a website’s success. As the world’s leading search engine, Google offers a powerful channel for increasing website visibility and acquiring targeted traffic, making it essential to master its SEO (Search Engine Optimization) strategies. This article, "The Underlying Logic and Best Technical Practices of Google SEO Traffic", will systematically analyze how search engines work and operate, helping you understand how they rank content through algorithms and signals. In addition, we will dive into essential areas such as technical SEO implementation, keyword research, content architecture planning, topic development, content quality optimization, and link building—unveiling a full-chain optimization strategy from foundational logic to practical execution. The article also summarizes SEO concepts and key points, analyzes common issues and their solutions, and empowers you to stand out in the competitive search engine landscape. Whether you’re an SEO beginner or a seasoned optimization expert, this article will provide you with actionable strategies and practical tools to steadily increase your website traffic and achieve more efficient search engine visibility.
The article “The Underlying Logic and Best Technical Practices of Google SEO Traffic” provides a well-organized table of contents for readers. As the article is quite lengthy, it is recommended to bookmark it and read it sequentially when time permits or when needed. This reading method is more conducive to forming a systematic understanding of SEO; otherwise, fragmented reading may make it difficult to grasp the logical relationships between each part. Of course, you can also skip the suggestion and click the blue anchor text links in the table of contents to jump directly to the specific sections for targeted study.
- Understanding Google Search Engine
- Technical SEO
- TDU Tags
- Property Tags
- Robots Protocol (robots.txt)
- Sitemap (XML Sitemap)
- SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
- Nofollow and Dofollow
- Canonical Tags
- Index and Noindex Tags
- Schema
- Hreflang Tags
- Alt Text
- Website Structure (Navigation Menus)
- SEO-Related Status Codes
- Submitting a Site to Search Engines
- Checking the Number of Pages Indexed by Search Engines
- Submitting New Pages or Updated Content
- SEO Keyword Research
- SEO Content Planning
- SEO Topic Strategy
- SEO Content Quality Evaluation Metrics
- Ranking Signals for Page Improvement
- SEO Link Building
- Reasons for SEO Traffic (Ranking) Drops and Solutions
- Ways to Improve SEO Click-Through Rate (Increase Traffic)
- Optimize Keywords in Titles and Descriptions
- Use Attractive Title and Description Formats
- Use Rich Media (Videos, Images) to Enhance Search Result Displays
- Include Dates or Update Times
- Use Clearer and More Descriptive URLs
- Add Structured Data
- Improve Page Load Speed
- Optimize for Local Search (How to Add Google My Business Info)
Ⅰ、Understanding Google Search Engine

The methodology for effective Google SEO, like anything else, requires careful planning before action. SEO is not simply about keyword stuffing or blindly pursuing the number of backlinks; it is a systematic strategic process. Before beginning the optimization work, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the principles and operational mechanisms of the Google search engine. The core of Google’s search engine lies in its complex algorithms, which are designed to provide users with the most relevant and valuable content. Understanding these algorithms can help us more accurately pinpoint the direction of optimization and grasp the essence of Google SEO. Success in Google SEO is not accidental; it is built on a deep understanding of the search engine's principles and operational mechanisms. Only by truly understanding how Google’s search engine works and recognizing its patterns can we position ourselves advantageously in the complex and ever-changing search environment, achieving a win-win for both website traffic and business conversions.
Understanding the Google search engine is the first step towards effective SEO optimization. The core mission of a search engine is to provide users with accurate, high-quality answers that meet their search needs. Its existence is fundamentally to answer people’s questions, not to cater to the optimization strategies of website owners or SEO experts. Whether it’s a simple query or a complex information need, Google is dedicated to presenting the most valuable content to users through its algorithms. Compared to SEO experts, search engines have a much deeper and more comprehensive understanding of users. It relies on its massive data analysis capabilities to track and analyze global search behavior in real-time, gaining insights into users’ search intent and preferences. Based on this data, Google continually adjusts and optimizes its algorithms to ensure that each search result can best meet users' needs. Therefore, attempting to rely solely on technical tricks while neglecting the quality of the content itself is often counterproductive.
The focus of the Google search engine is to provide useful answers, not to passively accept various ranking techniques. While proper SEO techniques can help a website be better recognized and understood by search engines, the real key to ranking lies in the relevance, authority, and user experience of the content. The design of search engine algorithms is intended to reward websites that focus on providing real value to users, rather than those that only emphasize external optimization methods. Additionally, Google has a zero-tolerance policy for deceptive practices and will take strong action against attempts to manipulate search results. This includes techniques like keyword stuffing, hidden text, and malicious linking. Once violations are detected, a website may face penalties such as ranking drops or even complete removal from the search engine. Maintaining transparency, fairness, and focusing on creating high-quality content for users is the correct path to achieving long-term SEO success. Understanding the essence and operational mechanisms of the Google search engine is essential knowledge for every SEO professional and website administrator. Only by truly standing in the users' shoes and creating valuable content can one gain an advantage in the highly competitive search environment.
1、The Timeliness of Google Search Engine

(1) Before 2015: The Era of Keyword Matching
The development of Google’s search engine has gone through different era stages, reflecting the continuous evolution of technological advancements and user demands. Before 2015, the Google search engine primarily operated in the keyword-matching era. During this stage, the core algorithm of Google’s search engine relied on precise matching of the keywords input by the user. The focus of website optimization was on how to strategically place keywords on the page to improve search rankings. Although this method was simple and effective, it also led to the proliferation of low-quality content, with many websites attempting to manipulate rankings through keyword stuffing, ignoring the actual value of the content itself.
(2) After 2015: The AI Era of Content Relevance to User Needs
With advancements in technology and the diversification of user demands, after 2015, search engines entered the era of artificial intelligence (AI). In this stage, search engines like Google no longer relied solely on keyword matching but instead placed greater emphasis on the relevance of content to user needs. The introduction of AI technology enabled search engines to understand semantics and analyze context, allowing for a more accurate grasp of user search intent. This shift led to profound changes in SEO optimization strategies, with content quality, user experience, and the actual value of the page becoming key factors affecting rankings. The transition of Google’s search engine from simple keyword matching to AI-based semantic understanding marked its shift from a tool-based platform to an intelligent information service. This era-defining transformation not only improved the precision of search results but also encouraged content creators to focus on providing genuinely valuable information to meet users' increasingly diverse needs.
2、How Google Views External Links (Backlinks)

Google Search Engine Algorithm considers external links (backlinks) as a key factor in evaluating the value and credibility of a webpage. When other websites link to your page, it is essentially casting a “vote of trust” for your content, signaling to search engines that the link has a certain level of value and reliability. This kind of external endorsement helps search engines determine the authority and influence of your website within a specific topic area. Moreover, backlinks are not only a technical optimization method; they also provide readers with additional contextual information, helping them better understand related topics. High-quality backlinks typically appear on pages with strong content relevance, serving as sources of supplementary information, and enhancing the user’s reading experience and ability to obtain information. Finally, backlinks often function as a form of recommendation. When a website reviews a particular product or service and includes a link to that product or service page, it acts as a recommendation to the reader. This kind of natural recommendation link not only helps increase the credibility of the linked page but also strengthens the user’s trust in the recommended content. Therefore, when evaluating backlinks, Google’s algorithm pays attention not only to the quantity but also places greater emphasis on the quality, relevance, and authority of the link source.
3、Who Is SEO Content Written For?
Who Is SEO Content Really Written For? The Answer Is Actually Quite Simple — It’s Written For Both Humans And Machines. These two are not mutually exclusive but are complementary and inseparable. In the context of modern search engine optimization, high-quality content must first attract and engage readers, meet their needs, answer their questions, and provide valuable information. After all, real traffic and conversions come from user approval. Only content that resonates with the audience and sparks interest can prompt readers to stay, click, and even share. However, if content solely caters to users while ignoring Google Search Engine’s rules, it will be difficult to achieve good rankings in fierce competition. The Google Search Engine relies on algorithms and GoogleBot (Crawler) Programs to understand and index web pages, ensuring that users receive the most relevant results quickly when searching. Therefore, SEO content must also consider how machines “read” it, by applying proper keyword placement, optimized heading structures, metadata settings, and internal linking strategies to help search engines better crawl and understand the core information of a page.
In practice, content creators need to find a balance between the two. They must skillfully incorporate keywords and technical optimization elements without compromising the reading experience. One could say that the art of SEO lies in this balance—it is a "dual communication" between humans and algorithms, needing to resonate with people while also catering to logic. Only when the content excels in both aspects can the ultimate goal of search engine optimization be truly achieved.
4、How the Google Search Engine Works
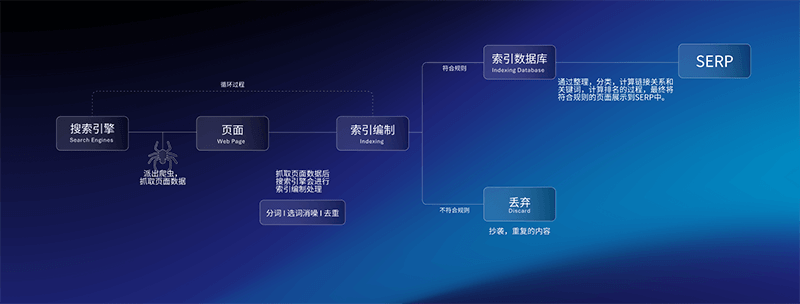
The example image above illustrates how the Google search engine works. This process forms a continuous cycle, where the Google search engine constantly crawls new data and updates its index to ensure the timeliness and accuracy of search results. The operation of the Google search engine can be broken down into the following key steps:
- Search Engine Crawls Page Information: Search engines deploy web crawlers (such as GoogleBot) to gather webpage data. These crawlers automatically traverse the internet, collecting content information from webpages to ensure that the search engine has the most up-to-date data.
- Search Engine Processes Page Information: The data collected by the web crawlers is sent to the search engine for processing. The content of the webpage includes text, images, links, and more, and the crawler attempts to capture as much usable information as possible from the page for further processing.
- Search Engine Indexing: The data collected from the pages enters the indexing stage. This phase includes tokenization, keyword selection, noise reduction, and deduplication, among other processes, so that the search engine can efficiently understand and store the webpage content. The goal of indexing is to structure large amounts of webpage data, making it easier and faster to retrieve.
- Search Engine Index Database: The completed index is stored in the index database. This database organizes and categorizes the data, calculates link relationships, and applies ranking algorithms. Content that meets the criteria is retained, allowing search results to be presented quickly when users search.
- Discard: Content that does not meet indexing rules, such as plagiarized or duplicate webpages, is discarded to prevent it from appearing in search results. This step ensures the quality of search results and prevents low-quality or irrelevant content from interfering with the user experience.
- SERP (Search Engine Results Page): Ultimately, the content that has been indexed and filtered will be displayed on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). After users enter a keyword, the search engine will match it against data in its index database and display the most relevant results.
5、Google Search Engine Algorithms and Signals
There is a close relationship between signals and algorithms, as they can influence each other and together form key parts of many systems and processes. In many cases, algorithms rely on signals to make decisions and perform actions. An algorithm refers to a set of rules used in a search engine to process and rank web pages, while signals are the data and features used to measure the quality and relevance of a webpage. These signals (information) are fed back to the algorithm. When a search engine receives a user's query, it uses algorithms to analyze information such as the webpage content, link structure, and user behavior. These pieces of information are signals. The algorithm uses these signals to determine which web pages are the most relevant and ranks the search results accordingly. Therefore, the search engine’s algorithm relies on signals to assess the relevance and quality of a webpage, while signals are the input data for the algorithm. Together, they work to enable the search engine to provide the most relevant search results for users. Below are the key algorithms and signals of the Google search engine:
(1) Google search engine’s core algorithm
PageRank Algorithm
PageRank was developed in 1997 by Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin. It was designed to evaluate the quality and quantity of page links. Along with other factors, this score determines a page’s position in search engine rankings. Since 2013, PageRank has no longer publicly disclosed official data on domain authority, and it has since remained a hidden algorithm within Google’s internal system. Currently detectable metrics such as DA, PA, DR, and UR are results derived from third-party SEO data analysis tools that reference the former official algorithm. Each tool has slightly different evaluation parameters for authority, which explains why there are variations in the authority scores assessed by different tools. The primary function and operating mechanism of the PageRank algorithm are as follows:
①The main function of PageRank algorithm:
- SERPs Click-Through Rate: The higher the natural click-through rate of Google search results, the higher the page's ranking typically is.
- Link Voting: The PageRank algorithm is based on the principle of "link voting," where a webpage votes to support the importance of another page by linking to it.
- Link Quality: Not all links carry the same weight. Links from high-quality, authoritative pages are more valuable than those from low-quality pages.
- Link Quantity: In addition to link quality, the quantity of links is also a factor. More external links generally improve a webpage's ranking in Google search results.
- Internal Links: Internal links are also considered important. While the voting weight of internal links is not as high as that of external links, they still play a role in keyword voting.
②The operating mechanism of PageRank algorithm:
- Link Authority Transfer (Link Juice Transfer): The PageRank algorithm measures the authority and importance of web pages through the transfer of authority, also known as “Link Juice.” When one webpage links to another, it passes part of its own authority to the linked page, helping search engines determine the value of that page.
- Recalculation Cycle: PageRank values are not static; they are recalculated periodically to reflect the latest link relationships.
RankBrain algorithm
RankBrain is one of the core algorithms of the Google search engine, based on machine learning technology. Its purpose is to help Google process search queries more intelligently, especially those that are new or uncommon. It is able to understand the relationship between user search intent and keywords, enhancing the relevance and accuracy of search results. The main functions and operation mechanism of the RankBrain algorithm are as follows:
①The main functions of the RankBrain algorithm:
- Understanding Search Intent: The ability to analyze the true needs behind a user's search, not just relying on keyword matching.
- Handling Unfamiliar Queries: For new or uncommon search terms, RankBrain can infer relevant search results based on existing data.
- Optimizing Search Result Ranking: By learning from user clicks and interactions, search result rankings are continuously adjusted to improve user experience.
- Enhancing Semantic Understanding: Better understanding of synonyms, phrase structures, and their context to provide more logically accurate answers.
②The operating mechanism of RankBrain algorithm:
- Data Analysis and Learning: Collecting large amounts of search data and training machine learning models to understand the relationships between different search terms and webpages.
- Feature Matching: When processing search queries, RankBrain analyzes the features of the keywords and looks for content that is semantically related.
- Dynamic Ranking Adjustment: Based on user behavior data, such as click-through rate and time spent on a page, search result rankings are optimized in real-time to ensure more relevant content appears first.
- Self-Optimization: RankBrain constantly learns new search patterns and automatically improves the algorithm's performance to adapt to changing user search behavior.
Panda Algorithm
The Panda algorithm is an important search ranking update launched by Google in 2011, aimed at penalizing low-quality content websites and boosting the rankings of high-quality content. It primarily determines rankings by evaluating the quality of a website's content, encouraging original, in-depth, and user-value-driven content, thereby improving the overall search results experience. The main functions and operation mechanism of the Panda algorithm are as follows:
①The main functions of the Panda algorithm:
- Lowering Rankings for Low-Quality Websites: Reducing the visibility of websites with duplicate content, plagiarism, keyword stuffing, excessive ads, etc., in search results.
- Promoting High-Quality Content: Encouraging original, in-depth, informative, and user-helpful pages to achieve higher rankings.
- Fighting Content Farms: Addressing websites that generate traffic through the massive accumulation of low-quality content, reducing their weight in search results.
- Improving User Experience: By filtering quality content, the accuracy and efficiency of users' ability to find information through search engines are enhanced.
②The operating mechanism of Panda algorithm:
- Content Quality Evaluation: Scoring website content based on originality, depth, readability, relevance, and other factors.
- Quality Scoring Model: Using machine learning models to classify high-quality and low-quality content, forming a "quality score" that impacts a website's ranking in search results.
- Site-Level Impact: Panda evaluates not only individual pages but also considers the overall content quality of the entire website. Too many low-quality pages can impact the website's overall ranking.
- Regular Updates: Initially released as periodic updates, Panda has since been integrated into Google's core algorithm, having a real-time impact on search rankings.
- User Signal Reference: Combining user behavior data (such as bounce rate, time on page, etc.) to further verify the actual value of a page's content.
Penguin algorithm
The Penguin algorithm is a search ranking update launched by Google in 2012, primarily aimed at combating websites that manipulate search rankings using Black Hat SEO techniques, especially targeting unnatural external links (backlinks) and over-optimization practices. Its core goal is to enhance the fairness of search results by ensuring that website rankings are based on genuine content quality and user value, rather than achieved through manipulative tactics. The Penguin algorithm emphasizes the naturalness and quality of backlinks, encouraging websites to focus on content development and user experience, and to avoid gaining ranking advantages through unnatural methods. The main functions and operating mechanisms of the Penguin algorithm are as follows:
①The main functions of Penguin algorithm:
- Combat Unnatural Links: Target backlinks acquired through unnatural means such as paid links, Link Farms, and link exchanges, reducing their impact on rankings.
- Penalize Over-Optimization: Lower the rankings of websites that engage in SEO manipulations such as keyword stuffing and excessive optimization of Anchor Text.
- Increasing the Value of Natural Links: Encouraging websites to naturally gain backlinks through high-quality content rather than relying on manipulative techniques.
- Real-Time Monitoring of Link Quality: Later versions of the Penguin algorithm were integrated into Google's core algorithm to assess a website's link quality in real time, reflecting in search rankings immediately.
- Precise Penalties: Instead of penalizing an entire website, penalties are now applied more precisely to specific pages or links.
②Operation mechanism of Penguin algorithm:
- Link Quality Analysis: The algorithm detects the sources of external links (backlinks) to a website and evaluates whether the links are relevant, authoritative, and natural.
- Anchor Text Evaluation: The distribution of anchor text in backlinks is checked to identify whether there is any unnatural keyword stuffing or over-optimization.
- Bad Link Identification: Identifying low-quality or manipulative links, such as link farms, spammy directories, and irrelevant forum comments, and reducing their weight.
- Real-Time Algorithm Updates: Since the release of Penguin 4.0, the algorithm has been integrated into Google's core algorithm, processing link data in real-time and reflecting changes quickly in search rankings.
- No Direct Penalty, Just Ignored: The latest version no longer directly penalizes violating links but instead "ignores" their influence, reducing their positive impact on rankings.
- Encouraging Self-Cleanup: Website administrators can use the Disavow Tool to reject bad links or actively clean up unnatural links, helping to restore the site's ranking.
(2) Google search engine signals
Google Search Engine Signals refer to the various factors and data that the algorithm considers when evaluating web page rankings. These signals help Google assess the relevance, authority, and user experience of a webpage in order to provide users with the most accurate and valuable search results. Search engine signals can be categorized into multiple dimensions, including content quality, domain, Keywords, social media, external links (backlinks), user behavior (user experience), technical performance, and page structure, among others. For example, high-quality original content, valuable external links, good click-through rates, page loading speed, and mobile responsiveness are all important signals that influence rankings. In addition, Google also considers technical factors such as page security, HTTPS encryption, URL structure, and internal link optimization. Search engine signals do not function independently but are interconnected and comprehensively evaluated through complex algorithmic models to ensure that search results accurately meet user queries. As technology continues to evolve, Google is constantly adjusting and refining the weight of these signals to adapt to changes in user search behavior and the content ecosystem. The types and details of Google Search Engine Signals are as follows:
Domain Signals
Among the many ranking signals in Google's search engine, the Domain Name signal is one of the factors that affect a website's search performance. Domain authority refers to the overall influence and credibility of a domain in search engines, which is typically influenced by multiple aspects such as historical site performance, the quality and quantity of external links, and content quality. A domain with high authority often indicates that the website has greater credibility and authority within its industry, which can help it achieve better rankings. Domain age is also a signal worth noting. Although Google has officially stated that its impact is limited, websites that have been active for a long time and consistently maintain high-quality content are usually considered more stable and trustworthy, thereby gaining some ranking advantages. Additionally, the transparency and consistency of domain registration information are also evaluated. Public and credible registration details can enhance the trust of search engines in the website, while frequent changes or opaque privacy-protected information may raise concerns. Overall, the domain name signal plays a supporting role in Google's search algorithm and works together with other signals such as Content Quality and user experience to determine a website’s performance in search rankings.
Keyword Signals
In Google’s search engine ranking mechanism, keyword signals are one of the important factors for evaluating the relevance of a webpage. The frequency and density of keywords can help search engines determine how well a webpage matches the user’s search intent. Proper keyword density can reinforce the focus of the page's theme and improve its visibility in related searches, but overusing keywords can be seen by the algorithm as keyword stuffing, which may negatively impact the ranking. In addition to frequency and density, the specific placement of keywords on the page also plays a crucial role. Incorporating keywords strategically into the title (Title Tag), body content, heading tags (such as H1, H2, H3), and URL can enhance search engines’ understanding of the page’s theme and improve its ranking potential in related search results. Especially in the title and URL, keywords help both search engines crawl and index the page while attracting user clicks, further increasing the page’s click-through rate and exposure. However, Google’s algorithm places more emphasis on natural and fluent content expression, stressing the balance between reasonable keyword placement and content quality, avoiding mechanical keyword stuffing strategies. As algorithms continue to evolve, keyword signals are no longer the sole determinant of ranking but instead work in conjunction with other factors like content relevance and user experience to ensure higher-quality search results for users.
User Experience (UX) Signals
In Google's search ranking algorithm, user experience (UX) signals are an important reference factor for measuring webpage quality and user satisfaction. Page loading speed is one of the key metrics affecting user experience. Fast-loading pages effectively reduce bounce rates, increase user engagement, and result in better search rankings. Mobile-friendliness is also critical. With the continued growth of mobile search traffic, Google emphasizes a website's ability to adapt to different screen sizes to ensure that mobile users have a smooth browsing experience. Click-through rate (CTR) reflects how much interest users have in a particular page in the search results. A higher CTR usually indicates that the page's title and description are attractive, which helps improve rankings. Dwell time measures how long users stay on a page after clicking a search result. A longer dwell time typically indicates that the page content aligns well with the user's search intent. Related to this is the "Pogo Stick" phenomenon, where users click on a search result, quickly return to the search page, and click on another link. This may suggest that the page failed to meet the user's needs, potentially negatively impacting the ranking.
In addition, a flat website structure helps reduce the number of clicks users need to make when finding information within the site, improving navigation efficiency. Breadcrumb navigation provides clear path indications, helping users quickly understand the hierarchical relationship of the current page within the website, thereby enhancing the site's usability. User comments and site reputation are also important UX signals. Positive user feedback and a good brand reputation can enhance search engines' recognition of the website's credibility. Finally, Google also considers Chrome bookmark data. Pages that are frequently bookmarked by users may be seen as having higher value, thus indirectly influencing rankings. Overall, user experience signals not only directly relate to user satisfaction but also serve as an important basis for Google to measure webpage quality and optimize search results.
Link signal
In Google's search ranking algorithm, link signals are one of the important factors for measuring a webpage's authority and content relevance. The quality and quantity of external links (backlinks) have a significant impact on rankings. High-quality backlinks typically come from reputable and authoritative websites, and are seen as a "vote" for the target page's content, effectively improving its visibility in search results. However, quantity is not the only standard; the relevance of the link, the authority of the source website, and the naturalness of the link are equally important. Low-quality or manipulated backlinks may be identified by Google's algorithm and can even lead to ranking penalties. The reasonableness of the internal linking structure helps search engines crawl and index website content more efficiently. A good internal link layout not only optimizes the crawling path but also helps distribute page authority (Link Juice), enhancing the ranking potential of important pages. Additionally, it improves the user browsing experience by making it easier for users to find more related content on the site, increasing page dwell time and interaction rates. Outbound links' quality and quantity are also an important part of link signals. A moderate number of outbound links pointing to high-quality websites can provide users with additional reference information, enhancing the webpage's content depth and authority. Google encourages a natural and reasonable outbound linking strategy, avoiding an excessive number of low-quality or irrelevant links that may negatively affect the site's credibility. Overall, link signals play an important role in Google's ranking system by connecting pages, transferring authority, and validating content value.
Technical Signals
In Google's search engine ranking algorithm, technical signals are core elements that ensure a website can be efficiently crawled, correctly indexed, and provide a good user experience. The structure and code quality of a website directly affect the crawling efficiency of search engine bots and the page loading speed. A clear structure and simple code help improve the search engine's understanding of the page content, thereby enhancing ranking performance. At the same time, whether the website uses a secure HTTPS protocol is also an important ranking signal. HTTPS encrypts data transmission to ensure user information security, and Google has explicitly included it in its ranking algorithm, encouraging websites to adopt a more secure online environment. Proper outbound dofollow link settings help search engines effectively recognize the weight transfer relationship between pages, enhancing the page's credibility. HTML errors and compliance with W3C validation are also crucial. Standardized code not only helps reduce page loading errors but also enhances compatibility across devices and browsers, improving the user experience. The Robots protocol (robots.txt) is used to control the access permissions of search engine bots to different parts of the website. Proper configuration can effectively guide search engines to focus on core content and avoid unnecessary crawling that wastes resources.
In addition, a sitemap (Sitemap) is an important navigation tool that helps search engines quickly discover and index all the important pages of a website, especially useful for websites with complex structures or newly launched sites. An SSL certificate is the foundation of the HTTPS protocol. It ensures the security of data transmission through encryption technology, enhancing user trust and the website's security rating. Technical signals play a fundamental and critical role in SEO optimization, providing a solid foundation for the website's accessibility, security, and search engine friendliness.
Content quality signals
In Google's ranking algorithm, Content Quality Signals are key factors in determining whether a webpage deserves to be displayed at the top of search results. Among these, E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is an important standard for evaluating content quality. Content that demonstrates real experience, professional knowledge, authoritative endorsements, and trustworthy sources is more likely to gain recognition from search engines, especially in sensitive fields such as health and finance. Originality and uniqueness are also core elements. Google tends to display content that is unique and offers original value, rather than simple copies or compiled information. Using canonical tags can effectively prevent issues with duplicate content, helping search engines identify authoritative pages and ensure SEO weight is concentrated on the right pages. Additionally, the depth and comprehensiveness of content are key indicators of quality. Articles that delve deeply into a topic and provide thorough information typically have a ranking advantage over superficial content.
The usefulness and value of content directly affect user experience, and Google encourages the publication of content that can truly solve users' problems or provide useful information. Proper use of bullet points and numbered lists can improve readability, helping users quickly access key information and enhancing the structured display of the page. Citing reliable references and sources not only increases the content's authority but also helps improve the search engine's trust. The freshness of content and its update frequency are also important quality signals. For time-sensitive topics such as news, technology trends, etc., Google prefers to display the most recent and relevant information. Even for evergreen content, regular updates can maintain its vitality in search engines, ensuring the accuracy and contemporary relevance of the information. Content quality signals determine whether content holds dual value for both search engines and users, making it a core element in SEO optimization that cannot be overlooked.
Social signals (mentions)
In Google's ranking mechanism, social signals (also known as mention signals) are not direct ranking factors, but they play an important supporting role in enhancing website authority and content credibility. Social signals mainly manifest in the sharing and discussion of content on social media. When an article or webpage is frequently shared, liked, or commented on across multiple platforms, it indicates that the content has high user approval and viral value. This widespread interaction can indirectly increase the page's exposure, attracting more organic traffic, which in turn has a positive impact on SEO. Additionally, a brand's reputation and activity on social platforms are also important signals. If a brand has a stable fan base, active interactions, and a good reputation on social media, search engines will consider the brand to have high credibility. This online reputation not only helps build user trust but also contributes to increasing the overall authority of the website, thereby influencing search rankings. Verifying the authenticity and credibility of a webpage or content through social media and other channels is also a key dimension of social signals. When content is mentioned or cited by authoritative media, well-known industry experts, or certified accounts, search engines tend to consider this information more reliable. This "endorsement effect" not only enhances the credibility of the content but also helps improve the website's visibility in search results. Social signals reflect real user feedback and approval of content, making them an effective reference for measuring webpage value.
6、Google Search Engine Penalties

Google search engine not only has the positive algorithm signals listed above but also includes penalty signals for detecting and penalizing cheating. When a website engages in manipulative behavior to try to manipulate Google search rankings, it may face penalties from the Google search engine. These cheating behaviors include, but are not limited to, keyword stuffing, hidden text and links, purchasing backlinks, mirror websites, and automatically generating low-quality content. Once detected by Google, the website may experience ranking drops, or in severe cases, some pages may be removed from the index, or the entire site may be completely excluded from search results. Google’s algorithm updates (such as Penguin and Panda) and manual review teams regularly check for violations to ensure the fairness and high quality of search results. After being penalized, a website must correct the issues and submit an appeal to potentially restore its rankings. The types of penalties, penalty results, penalty signals, and self-check methods for penalty outcomes are as follows:
(1) Types of Google search engine penalties
Manual Penalty
A manual penalty, as the name suggests, is a penalty decision made by a Google employee after reviewing a website. Google will send a notification to the site owner through the Webmaster Tools, outlining the general reason for the penalty and providing URL examples that violate Google’s quality guidelines. The site owner needs to fix the issues that violate these guidelines and then submit a re-evaluation request through the Webmaster Tools. Google employees will manually review the website again, and if it meets the requirements, the penalty will be lifted.
Algorithmic Penalty
If there is no notification in Google Webmaster Tools but the significant drop in rankings and traffic corresponds with the release date of an algorithm update, it is usually a result of an algorithmic penalty. Algorithmic penalties cannot be manually lifted. The only way to recover is to clean up the violations on the website and wait for the algorithm to recalculate the rankings.
(2) Google Search Engine Penalty Results
Mild
For violating websites, Google's penalty measures typically include domain devaluation, page devaluation, and ranking reduction. Domain devaluation refers to the weakening of the entire website's authority, leading to a significant drop in the ranking and traffic of all pages, affecting the overall search visibility of the website. Page devaluation is a penalty imposed on specific violating pages, causing those pages to drop in search rankings and reducing their exposure. Ranking reduction is the most common form of penalty, where violating pages are moved to lower positions in search results, resulting in a significant decline in click-through rates and traffic. Although these penalties do not lead to the complete removal of the website from the index, they directly impact the website's traffic and search performance, forcing webmasters to correct violations to restore rankings.
Severe
For websites that violate guidelines, Google's severe penalties are typically reflected in a significant drop in keyword rankings, with various forms and far-reaching consequences. Partial Keyword Penalty is one common scenario, usually occurring when the website’s core keywords are penalized, while secondary keywords and long-tail keywords remain unaffected. This type of penalty often results from the over-optimization of external links (backlinks) or the excessive accumulation of spam links. Especially, highly concentrated anchor texts are considered unnatural linking behavior, leading to a dramatic decline in the rankings of main keywords. Comprehensive Keyword Ranking Decline is a more serious form of penalty, involving a significant drop in the rankings of all keywords on the website, sometimes pushing them from the first page of search results to dozens of pages behind. Unlike normal ranking fluctuations, this kind of comprehensive drop is usually not due to algorithm updates or competitive pressure, but rather a clear penalty signal from the search engine, indicating that the website has committed serious violations.
(3) Google search engine penalty signal
- Low-Quality Link Types: If a large portion of external links (backlinks) comes from a single source (e.g., forum profiles, blog comments), they may be considered spammy links, indicating a low-quality website.
- Irrelevant 301 Redirects: Redirecting old URLs (that have earned backlinks and referring domains) to new pages unrelated to their content (e.g., redirecting old blog posts to the homepage) may be seen by Google as a soft 404, failing to effectively pass link value.
- Broken Links (404 Errors): A website with a significant number of broken links (404 error pages) is considered poorly maintained, lowering user experience, which can subsequently affect rankings.
- Too Many Affiliate Links: A website containing an excessive number of affiliate marketing links (Affiliate Links) is likely to be considered overly commercialized, which can negatively impact the site's authority and trustworthiness.
- Lost External Links: A continuous decline in the number of backlinks may signal a decrease in a website's popularity, leading to a significant drop in rankings.
- Excessive Link Exchanges: Frequently exchanging links with other websites, especially for links with no real value, is considered a violation by Google and may trigger penalties.
- Pop-up or Disruptive Ads: According to Google's official guidelines, frequent pop-up ads or ads that disrupt user experience are considered signs of a low-quality website, potentially affecting page scores.
- Over-Optimization of Keywords: Keyword stuffing, repeating keywords excessively in title tags, or over-optimizing page content are recognized by Google as unnatural SEO practices, which can lower page rankings.
(4) Self-checking method for Google search engine penalty results
Self-check Method 1 for Search Engine Penalty: Use the "site" command to query the domain
Using the Site: Operator to query a domain is a commonly used self-check method to determine whether a website has been penalized by search engines. By entering site:yourdomain.com (replace yourdomain.com with the actual domain) into the Google search bar, you can view the number and range of pages indexed by Google for that website. If the search results are empty or the number of indexed pages has significantly decreased, it may indicate that the website has been de-ranked or removed from the index by the search engine.
Self-check Method 2 for Search Engine Penalty: Search for the Website Name
Another effective self-check method to detect if a website has been penalized by the search engine is to search for the website’s name. Simply enter the brand name or company name in the Google search box and check if the website appears in the search results. If the website does not appear on the first page of results for the brand name search, especially if the official website is not prioritized, it may indicate that the website has been penalized or demoted by the search engine.
Self-check Method 3 for Search Engine Penalty: Check the Number of Indexed Pages in Google Search Console
Here is the complete English translation with all HTML tags preserved and inner Chinese content translated into English with capitalized tag text: --- Using the Google Search Console (GSC) to check the number of indexed pages is a crucial self-diagnosis method for detecting whether a website has been penalized by search engines. After logging into GSC, go to the "Coverage" or "Pages" report to visually view the number of indexed pages and changes in indexing status. If a sudden and significant drop in indexed pages is observed, or a large number of pages are marked as "Excluded," it may be a sign of algorithmic penalties or technical issues on the site. In addition, GSC provides detailed information about indexing errors, crawl anomalies, and manual actions, helping webmasters quickly identify problems. Regularly monitoring this data can help detect potential risks early and take corrective measures to ensure the website's visibility in search engines.
Self-check Method 4 for Search Engine Penalty: Comprehensive Tracking of Keyword Rankings
Here is the full English translation of your text with all HTML code tags preserved, including translated Chinese content within the tags (with capitalized tag text as requested): --- Comprehensively tracking keyword rankings is one of the important self-check methods to determine whether a website has been penalized by search engines. By using keyword ranking tracking tools such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz, etc., webmasters can continuously monitor the ranking fluctuations of core keywords in search engines. If certain important keywords suddenly experience a significant drop in ranking—especially if they fall to a much lower position or drop from the first page to subsequent pages—it may indicate that the website has been penalized by search engines. Compared to normal ranking fluctuations, a penalty-induced drop is usually more drastic and persistent. By regularly reviewing ranking trends, webmasters can detect potential penalty risks in a timely manner, analyze the reasons, and take corrective actions.
Ⅱ、Technical SEO
Technical SEO is a key factor in improving a website's ranking in Google search results and involves a variety of technical optimization strategies. First, the proper use of HTML Tags (such as Title, Meta Description, H1, Alt, etc.) can help search engines better understand the content of a page, thus improving indexing efficiency. In addition, integrating JSON-LD Format Structured Data (Schema Code) provides a clear data structure to search engines, increasing the chances of rich search result features (such as star ratings, FAQs, etc.). In terms of site architecture, a well-designed Website Structure not only enhances user experience but also allows search engine crawlers to efficiently index content. It is recommended to use a clear internal link hierarchy and breadcrumb navigation. At the same time, ensuring the site returns the correct HTTP Status Codes (such as 200, 301, 404, etc.) is crucial to help search engines properly identify page status and avoid the negative impact of broken links or duplicate content.
From a performance perspective, the Page Size Should Be Kept Under 15MB, as Google's crawler may not fully fetch pages exceeding this limit, which can affect indexing coverage. In addition, enabling an SSL Certificate (HTTPS) has become one of the key factors in Google's ranking algorithm, ensuring the security of data transmission and enhancing user trust. Finally, by creating and maintaining a high-quality XML Sitemap, you can explicitly submit your website’s important pages to Google, helping search engines discover new content and accelerate index updates. By comprehensively applying these Google technical SEO strategies, you can effectively improve your website’s search visibility and strengthen its ranking advantage in highly competitive search results. The specific strategies required for Google technical SEO are as follows:
1、TDU Tags
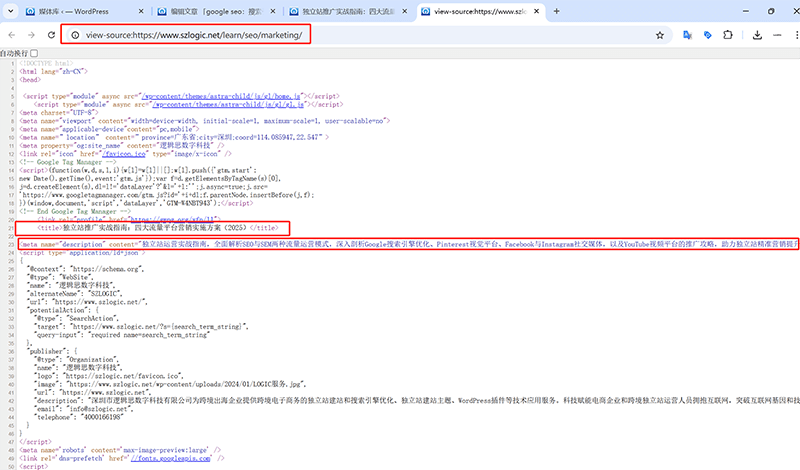
As indicated by the red box annotation in the front-end code example of the page above, TDU stands for the page’s Title, Description, and URL. When the page's keywords tag still played a role in SEO, it was also referred to as TDKU. However, on September 21, 2009, Google officially announced that it would no longer use the HTML meta keywords tag as a ranking factor. This information was released by Google's former Product Manager Matt Cutts through an Official Blog, clearly stating that Google's search algorithm does not reference the meta keywords tag to determine page rankings. As a result, meta keywords has essentially lost its practical value, and now most SEO professionals have simplified TDKU to TDU.
(1)title
The Importance of the Title Tag for Google SEO
The title tag is a crucial element in SEO, and its importance can be ranked as the highest. It is where we input the theme name (title) and strategically place core SEO keywords, directly affecting the page's ranking in Google search results.
Technical Implementation of the Page Title
The blogger’s Logic Digital Technology is a company focused on the full ecosystem of WordPress technology development. It integrates WordPress Web Design and development, and has been deeply engaged in research and work related to the backend technology stack based on PHP. In actual development, the output of front-end page information, including title data, is implemented through PHP’s dynamic data processing and rendering. Outputting information on the front-end page is a typical implementation scenario of backend programming technology. In the WordPress environment, PHP calls functions within the theme templates (such as wp_title() or the_title()) to output the title. To improve development efficiency and code maintainability, developers can also combine custom functions, Hooks, and Filters to flexibly adjust the output logic of the title.
Title Tag Writing Guidelines
When performing Google SEO optimization, the page’s title tag plays a crucial role. It is not only a core element for search engines to understand the page content but also a key factor in attracting user clicks. Therefore, writing a high-quality title requires following certain guidelines to improve both the page’s ranking and click-through rate. First, the page title should Align With User Search Intent. This means that when crafting the title, you must think from the user's perspective and understand what information they truly want when searching for a specific keyword. The title should accurately summarize the core content of the page, ensuring users can quickly determine whether it meets their needs when viewing the search results. Secondly, Including Core Keywords is essential for enhancing SEO effectiveness. Integrating highly relevant core keywords into the title helps search engines better understand the theme of the page, thereby improving its ranking in related search results. However, the inclusion of keywords should be natural and smooth, avoiding keyword stuffing, which can harm both user experience and search engine evaluation. In addition to satisfying search intent and keyword optimization, the title should also Attract User Clicks. A click-worthy title often sparks user interest, arouses curiosity, or meets a specific need. You can enhance title appeal by adding emotionally engaging words, numbers, unique selling points, or compelling descriptions, thereby boosting the click-through rate. Finally, Keeping The Title Length Within 29 Characters helps ensure it is fully displayed in search results without truncation, which could negatively affect readability. Although the character display limit may vary across different devices, keeping the title concise, clear, and on-point significantly improves readability and visual impact, enhancing overall SEO performance.
(2)description
The Importance of the Description for Google SEO
The description, also known as the meta description, is an HTML meta tag used to briefly summarize the content of a webpage. However, Google does not use the meta description as a direct ranking factor for keywords. Despite this, a well-crafted custom meta description still holds significant value, even though it may not always be 100% adopted by the search engine for display in search results (SERP). In some cases, Google may automatically extract what it deems the most relevant text snippet from the page content based on user search intent to display as the description. Even so, a well-structured and engaging meta description still has a high chance of appearing in the SERP, helping users quickly understand the page content and increasing click-through rates.
Technical Implementation of the Page Description
The technical implementation of the description is similar to the title tag. It is typically developed using PHP and is dynamically generated through WordPress built-in functions. In the theme's functions.php or header.php file, code can be written to add a custom meta description input field in the backend, dynamically rendering the meta description to the frontend of the page. This approach not only improves SEO control over the page but also allows flexible management of different pages' meta descriptions.
Meta Description Writing Guidelines
The page's Description (Meta Description) is used to briefly summarize the content of the webpage. Writing an effective meta description requires following certain guidelines. First, control the character length. It is recommended to keep it within 155 English characters or 75 Chinese characters to ensure it is fully displayed in the search results page (SERP) without being cut off, which could negatively affect the reading experience. In addition, the meta description should closely focus on the core content of the page, accurately conveying the page's value and theme, helping users quickly understand the information. Properly embedding core keywords can improve search relevance. While it won’t directly affect ranking, it helps attract the attention of search users. The language of the meta description should be engaging, using concise and persuasive wording to spark user interest and avoid keyword stuffing or vague descriptions.
(3)URL
URL weight for Google SEO
The page's URL (Uniform Resource Locator) holds certain weight in Google SEO. While its influence is not as significant as core factors such as content quality and backlinks, properly optimizing the URL structure can still have a positive impact on both search rankings and user experience. First, a concise and clear URL is more beneficial for search engine crawling and indexing. A well-defined path structure helps Google better understand the page hierarchy and content theme, thereby improving the page's visibility in relevant searches.
Technical Implementation of Page URL Function
The fixed URL format is a native feature of the WordPress system, and it can be set in the WordPress site management dashboard under the "Settings" section in the left sidebar, specifically in the "Permalinks" option. Once the link format is fixed, you can customize the URL suffix in the article page management interface before publishing the page.
URL Writing Guidelines
Including core keywords in the URL can enhance the relevance signal of the page, helping search engines assess the alignment between the page content and user queries. While the role of keywords in the URL is relatively limited, in highly competitive search results, this small optimization may be the detail that influences rankings. Additionally, a concise URL can improve user click-through rates, avoiding long and complex parameters, making the link appear more trustworthy and professional. A good URL structure should also be logical and consistent, with recommendations to use hyphens (-) to separate words, and to avoid underscores (_) or meaningless characters. For dynamic URLs, it’s best to minimize redundant parameters, maintaining simplicity and readability. Overall, a well-structured, clear hierarchical URL with appropriate keywords not only aids SEO optimization but also enhances user experience and improves the overall accessibility of the website.
2、Property Tags
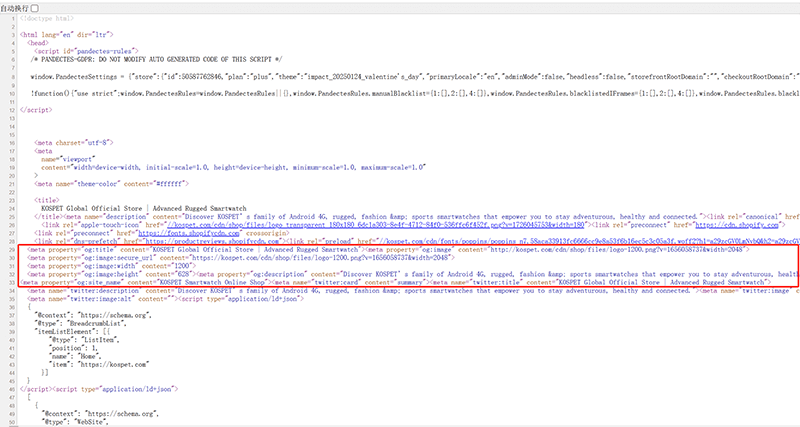
The meta property tag highlighted in the red box in the image above is the front-end code of the page. The meta property tag is related to the Open Graph (OG) protocol, which is used to optimize the way web content is displayed on social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc. Although these tags do not directly affect Google search rankings, they play an important role in improving the website's click-through rate and user interaction, which in turn indirectly positively impacts SEO.
By adding meta tags such as meta property="og:title", meta property="og:description", and meta property="og:image" to web pages, websites can control the display of the title, description, and image when shared on social media platforms. Well-optimized Open Graph tags can ensure that the content displayed when users share a webpage is more attractive, thereby increasing click-through rates and share frequencies. Higher social interaction may bring more external traffic, further increasing page exposure and user visits. Although Meta property tags do not directly affect Google search rankings, they indirectly enhance the page's appeal on social platforms, boosting website traffic, which positively impacts search engine rankings. Furthermore, the frequency of user clicks and shares is considered a signal of user behavior, and search engines may evaluate website content's quality and relevance based on these signals, thereby influencing rankings. Details of each type of meta property tag and the technical implementation for outputting meta property tag information to frontend page code are as follows:
(1) Types of Meta Property Tags
1、<meta property="og:locale" content="页面语言标签" />
2、<meta property="og:title" content="页面标题">
3、<meta property="og:description" content="页面描述">
4、<meta property="og:url" content="页面URL">
5、<meta property="og:site_name" content="网页名称" />
6、<meta property="og:image" content="图像的URL">(2) Technical Implementation of Meta Property Tags
To implement these tags, a custom function can be created in the header.php file to dynamically generate the necessary meta property tags. These tags are usually inserted into the head section of the page using the wp_head hook. When a page is accessed, the function dynamically outputs the corresponding Open Graph tags—such as og:title, og:description, and og:image—based on the page content. Furthermore, you can customize tag values according to different page types (e.g., posts, homepage, category pages) to ensure each page contains accurate metadata.
3. Robots Protocol (robots.txt)
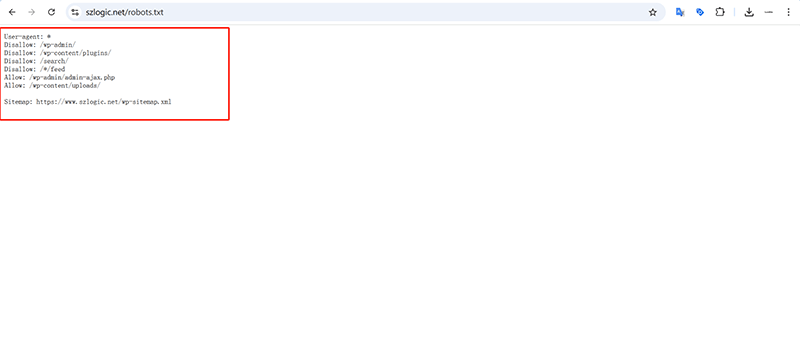
The robots protocol, also known as robots.txt, is shown in the red box in the image above, which contains the content of the robots.txt file. The robots.txt file is written in a simple text language. It does not require a specific programming language, but rather follows a set of rules known as the "Robot Exclusion Standard". These rules are used to tell search engine crawlers which pages or parts of the content can be accessed and which pages should not be crawled.
(1) Writing Guidelines for Robots Protocol (robots.txt)
If you are using a WordPress website, you simply need to copy and paste the following text code into the appropriate section of the dynamically generated robots.txt file within the WordPress directory to replace the existing content. For other website platforms or frameworks, users can customize the configuration based on their directory structure to specify which paths crawlers are allowed or disallowed to access. In this context, "Disallow" indicates that crawling is prohibited, while "Allow" means crawling is permitted. By default, if no specific "Disallow" directives are written, all paths are assumed to be allowed. Therefore, as long as the disallowed directories are clearly defined, it is not necessary to explicitly write "Allow" directives.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /wp-content/plugins/
Disallow: /search/
Disallow: /*/feed
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Allow: /wp-content/uploads/4、Sitemap (XML Sitemap)
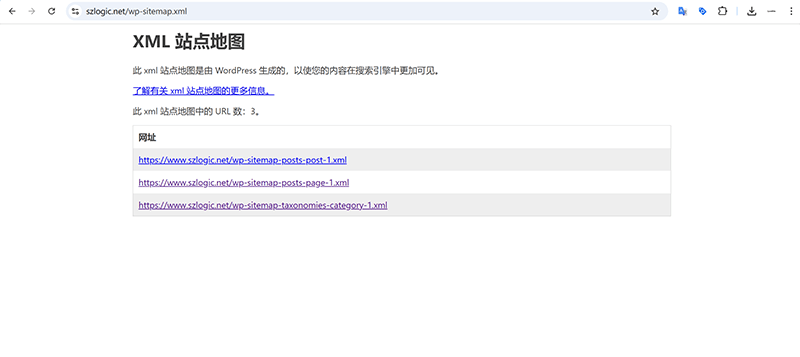
The example image above shows an indexable XML sitemap in WordPress. Under normal circumstances, every time a standard page or post is published, its URL is automatically included in the XML sitemap and categorized accordingly based on the type of content. The XML sitemap plays a critical role in SEO as it helps search engines crawl and index website content more efficiently. A sitemap is a file that contains links to all important pages on a website, usually provided in XML format, and is designed to clearly present the site's structure and content to search engines. Through the sitemap, search engines can more easily discover and index content that might not be linked from other pages, thus improving the overall visibility of the site. Sitemaps are especially important for large or newly launched websites because they ensure that crawlers do not miss any critical pages. They can also inform crawlers about details such as the update frequency and priority of each page, enabling search engines to schedule crawling tasks more intelligently. The existence of a sitemap not only speeds up the indexing process of new pages but also improves crawling efficiency, helping optimize search engine crawling strategies, which can indirectly enhance rankings and traffic. Additionally, submitting the sitemap to Google Search Console helps better monitor the site’s indexing status and identify potential crawling issues.
5. SSL Certificate (https)
.png)
The pop-up marked with a red box in the image above indicates that the website has successfully installed the SSL certificate and is secure. In contrast, the browser will show a security warning if it is not installed. The SSL certificate (Secure Sockets Layer) provides encrypted transmission to ensure the security of data exchanged between users and the website. It works by converting the HTTP protocol to HTTPS, creating an encrypted connection channel that prevents data from being intercepted or tampered with during transmission. In SEO, SSL certificates have become crucial, as search engines (especially Google) have explicitly made HTTPS one of the ranking factors. Websites with an SSL certificate typically gain an advantage in search rankings. Search engines assess a site's security based on whether it uses the HTTPS protocol, and HTTPS sites are considered more reliable and secure, thus enhancing user trust. This trust is critical for SEO because search engines are more likely to recommend secure sites, particularly in scenarios involving sensitive information exchange or online transactions. Whether for user experience or search engine ranking, SSL certificates help establish greater credibility for websites. Additionally, enabling HTTPS prevents the site from being flagged as "not secure," which could lead users to leave the site, negatively impacting bounce rates and user engagement, ultimately affecting SEO performance. Therefore, installing an SSL certificate not only enhances website security but also helps improve search engine rankings, thereby boosting overall SEO effectiveness.
(1) Technical Implementation of SSL Certificate Installation
In WordPress, installing an SSL certificate and enabling HTTPS is typically done through the site settings in a Linux-based control panel. Most hosting providers offer a graphical interface that allows users to easily apply for and install an SSL certificate directly from the control panel, making the process simple and convenient. If you are not using a Linux control panel, you can also manually apply for and install an SSL certificate through the Linux command-line interface. This process generally involves several key steps. First, the user needs to log in to the server and ensure that Certbot is installed. Certbot is a commonly used tool that helps users obtain free SSL certificates through services like Let’s Encrypt. After installing Certbot, run the command sudo apt-get install certbot. Depending on the web server used, additional plugins may be required—for example, sudo apt-get install python3-certbot-apache for Apache or sudo apt-get install python3-certbot-nginx for Nginx. Once installation is complete, users can use the certbot command to apply for the SSL certificate.
Execute the command `sudo certbot --apache` (or `sudo certbot --nginx`, depending on the web server used), and certbot will automatically detect and configure the SSL certificate, completing the application and installation process. During this process, the user needs to provide a valid domain name and ensure that the DNS record for that domain is correctly pointed to the server's IP address. Once the certificate is successfully applied, certbot will automatically configure Apache or Nginx to enable HTTPS. Additionally, certbot offers an automatic certificate renewal feature, allowing users to set up a cron job to regularly check and update the SSL certificate, preventing security warnings from appearing due to expired certificates. After the SSL certificate is successfully installed and HTTPS is enabled, users also need to adjust the site settings in the WordPress dashboard, updating the website address (WordPress address and site address) to a URL that begins with "https." Furthermore, it is strongly recommended to automatically redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS to ensure that all traffic is securely transmitted. This can be achieved by modifying the web server's configuration files (such as Apache's `.htaccess` or Nginx's configuration file) to ensure that unencrypted traffic is redirected to the encrypted version of the site.
6、Nofollow and Dofollow
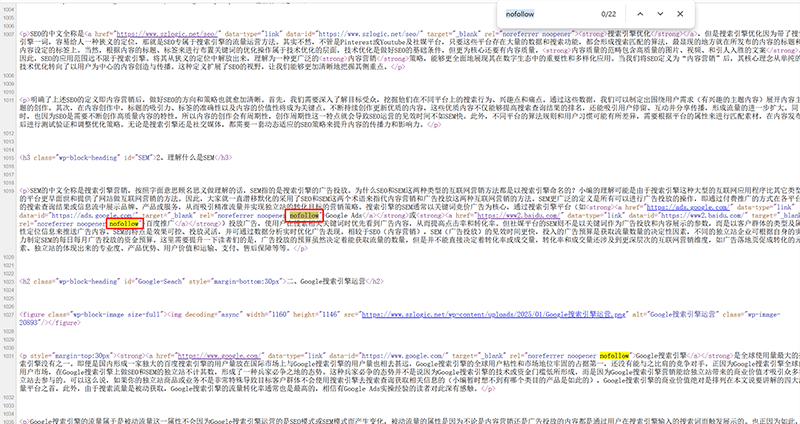
In Google SEO, nofollow and dofollow are two attributes used to instruct search engines on how to handle links on a page. They have different impacts on website rankings and crawler behavior, and understanding their roles is crucial for optimizing a site. Dofollow is the default setting, meaning that if the nofollow attribute is not explicitly applied, search engines will treat the link as a dofollow link. In other words, by default, Google will pass PageRank and other ranking signals through dofollow links. This allows websites to support the target pages they link to by passing authority, helping those pages rank higher in search results. Dofollow links are beneficial for SEO and are typically used for internal linking and for linking to important external resources.
In contrast, the nofollow attribute is used to tell search engines not to pass any ranking signals or authority through the link. Nofollow links do not influence the target page's ranking because Google does not treat them as valid voting signals. These types of links are commonly used in situations where passing link equity is not desired, such as external links in comment sections, advertisement links, or paid links. By using nofollow, websites can avoid passing authority to irrelevant or low-quality pages, thereby reducing the risk of spam or over-optimization.
(1) Technical Implementation of Nofollow
For websites built with WordPress.org, adding the nofollow attribute to outbound links requires no extra coding—WordPress natively supports this feature. Specifically, when adding anchor text in the post editor, there is an option to “mark as nofollow” in the link settings. On standard pages using Elementor’s page editor, you can also click the link settings button next to the link input field and simply check the “Add nofollow” option in the dropdown menu.
7、Canonical Tags
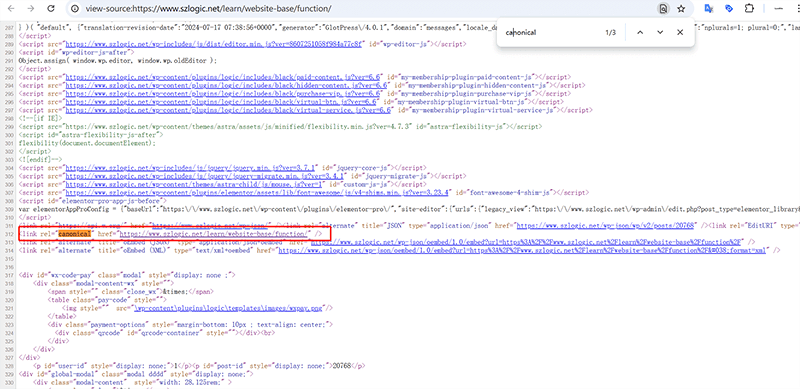
In the image above, the red box highlights the specific application of the canonical tag on an article page. The canonical tag is an HTML element that informs search engines about the preferred version of a page. When a website has multiple pages with similar or duplicate content, the canonical tag helps search engines identify the most authoritative version by pointing to the original page. Typically, the canonical tag is placed in the section of the page, linking to the original version’s URL, preventing search engines from being confused by duplicate content in indexing. In SEO, the canonical tag plays a crucial role. Firstly, it helps avoid duplicate content indexing issues, preventing multiple similar pages from affecting a site’s ranking. If search engines perceive similar pages as duplicate content, they might choose to index only one of the pages, ignoring the others, which would hurt the performance of those pages in search results. By using the canonical tag, a site can clearly tell search engines which page should be considered the original version, ensuring that all SEO value is concentrated on the preferred page.
The canonical tag can also optimize the site's link structure and traffic distribution, especially when multiple pages display the same content (such as product pages, category pages, or tag pages on eCommerce sites). By consolidating the authority to one main page, it helps improve the ranking of that page in search results. Additionally, it's important to note that ordinary pages don't frequently use the canonical tag because their URL structure typically only involves hierarchical relationships, rather than category or tag pages, thus avoiding multiple URLs. However, product pages and article pages are different; they often involve categories and tags. Therefore, product and article pages are the most frequent users of the canonical tag and are the pages that need special attention.
(1) Technical Implementation of the Canonical Tag
The implementation of the canonical tag follows the same principle as the title, description (meta description), and meta property tags mentioned above. It is achieved by using PHP to call WordPress built-in functions and utilizing hooks and filters. This process generates a canonical input field in the page management mode, where the filled URL is output to the front-end code, allowing search engine crawlers to crawl and index the page.
8、Index and Noindex Tags
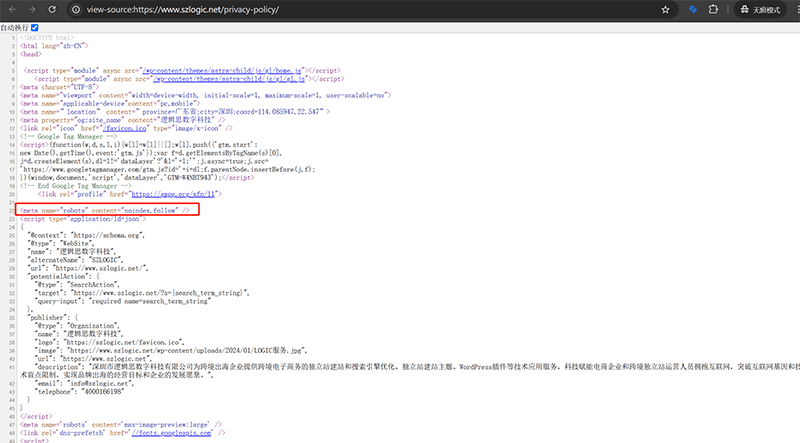
The front-end HTML code marked with a red box in the example above shows the actual application of the noindex tag. The "index" and "noindex" tags are used to control whether search engines should index the page's content. However, there is no need to specifically mark "index" on a page, as by default, if there is no "noindex" tag, it indicates that search engines are allowed to index the page's content, meaning the page's content will be added to the search engine's index and may appear in search results. On the other hand, the "noindex" tag tells search engines not to index the page, meaning the page's content will not be crawled or stored by the search engine, and therefore, will not appear in search results. In SEO, the "index" and "noindex" tags play an important role. Using the "index" tag ensures that the page can be indexed by search engines, improving its visibility in search results, which is the default setting for most pages. However, in some special cases, such as pages that have no value for search engines to crawl and index (e.g., login pages, thank you pages, privacy policy pages, etc.), using the "noindex" tag can effectively prevent these pages from appearing in search results, thereby focusing the search engine's crawling and indexing resources and avoiding irrelevant pages from affecting the overall SEO performance of the website.
(1) Technical implementation of the noindex tag
Similar to the programming logic of the other tags mentioned above, the `noindex` attribute for robots can be output to the front-end page code by writing the relevant output information code in the WordPress theme files.
9、Schema
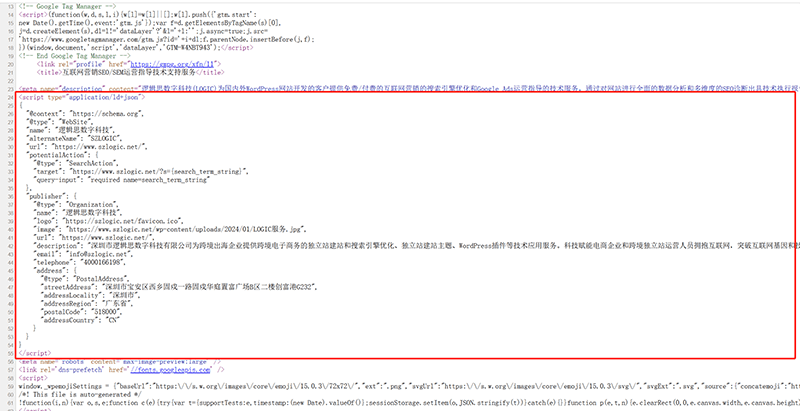
In the image above, the red box highlights the Schema code written and deployed to the page. As shown in the image, the Schema is written using JSON syntax. This structured data helps search engines better understand the content of the webpage, thereby improving the page's display in search results. Schema is not a single standard; it has two main types: Google Schema and Schema.org. There are some key differences between them, but their goal is the same: to optimize the presentation of website content in search engines and improve SEO performance.
(1)Schema.org
Schema.org is an open standard jointly promoted by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex and other search engines. Its purpose is to provide a unified framework for structured data, allowing different search engines to better understand and process webpage content. Schema.org offers a broader range of categories and attributes, suitable for various types of content such as articles, events, products, organizations, etc. It uses three formats—JSON-LD, RDFa, and Microdata—to represent data. Although Google Schema can also be considered a part of Schema.org, Schema.org, as an open standard, is more flexible and universal, suitable for multiple platforms and search engines.
(2) Google Schema
Google Schema is a structured data standard developed by Google for its search engine, typically used to provide more information in search results. For example, Google Schema supports formats like products, reviews, company information, etc., which can directly affect how search engines display information, such as rich snippets (rich snippets) or card-style search results. Google Schema typically includes specific fields and formats designed to directly support Google's search engine optimization and search result display features.
(3) Schema coding and deployment code
After selecting Google Schema or Schema.org, the next step is to write or modify the relevant Schema code according to the structured data syntax released by the official sources. Schema coding follows a specific JSON-LD format, which is the structured data format recommended by Google and other search engines. When writing the code, developers need to choose the appropriate Schema type based on the specific content type. For example, for article pages, the Article type can be used, and for company websites, the Organization type can be used. These types include several attributes such as name, URL, description, address, etc. Developers need to replace these fields with specific information relevant to their website content. After writing the structured data code, the next step is to deploy the code into the WordPress theme files. Typically, this Schema code is inserted into the header.php file, and it is output into the tags of every page. This way, whenever visitors load the site, the browser automatically loads these structured data, and search engines can crawl this information. In WordPress, the deployment process is not complicated, as the JSON-LD code can be directly embedded in the theme files or automated using plugins.
(4) Schema testing
After deploying the code to the frontend page, developers can use Google's structured data testing tool to check if the Schema is implemented correctly and whether rich snippets (such as ratings, reviews, events, etc.) are displayed successfully. Google's Schema testing tool is Rich Results Test, and Schema.org's testing tool is Schema Markup Validator. Both tools allow testing by using a URL or directly pasting the schema's JSON code. Schema (structured data) is crucial for improving a website's visibility in search engines because structured data not only helps search engines understand the page content but also enhances the display format of search results, thus improving click-through rates.
10、Hreflang Tags
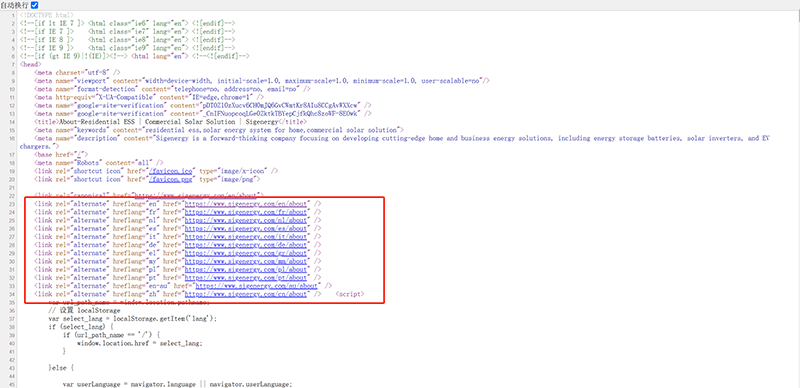
The specific syntax and arrangement format for outputting the hreflang tag information to the front-end page code is shown in the red box in the image above. The hreflang tag is an HTML element used to tell search engines the language and regional targeting of a specific page, helping search engines identify the appropriate content version for specific users. The hreflang tag is especially important for multilingual websites, as it clearly indicates which language or regional version of a page is intended for users in a particular region, ensuring the correct page version appears in search results. For example, if a website offers content in both English and Chinese, using the hreflang tag ensures that the English page is shown to users in English-speaking countries, while the Chinese page is shown to Chinese-speaking users. In SEO, the hreflang tag helps search engines avoid treating pages with similar or identical content as duplicate content, as different versions of a multilingual site may contain overlapping content. Without the hreflang tag, search engines may mistakenly index and display the wrong page version, which not only affects user experience but could also negatively impact SEO rankings. By properly using the hreflang tag, websites can increase their visibility in specific regions and languages, ensuring that each page is displayed to the correct target audience.
Additionally, the hreflang tag helps enhance search engines' understanding of website content, preventing SEO issues caused by language and regional errors. Correct implementation of the hreflang tag improves search engines' indexing efficiency for different page versions, boosting the ranking of that page in target languages and regions, which in turn increases targeted traffic. For websites targeting a global market, properly using the hreflang tag is key to optimizing cross-regional SEO.
(1) Technical Implementation of hreflang Tag
The hreflang tag does not require custom settings for each page. Typically, on multilingual sites, the hreflang tags for each page are consistent. Therefore, there is no need to write PHP functions or use hooks and filters to implement the front-end output. Instead, you can directly write the hreflang HTML code in the WordPress theme files.
11、alt text
Adding alt text (alternative text) to media files such as images and videos is a very important step. Alt text is the text content displayed by the browser when an image cannot be shown, and it also provides a description of the image content for search engines. It helps search engines understand the subject and content of the image and also improves website accessibility, especially for users with visual impairments. When using screen readers, users can understand the image's content through alt text. From an SEO perspective, alt text has a significant impact on the indexing and ranking of images. Search engine crawlers cannot "see" images like human users do, so alt text plays a crucial role in describing the image content. By providing relevant and accurate descriptions, search engines can better understand the image content and match it with related search queries. If the alt text of an image is closely related to the webpage content, search engines may display that image in image search results relevant to the search term, thus increasing traffic. Additionally, using keywords in the alt text appropriately can improve the overall SEO performance of the page. However, excessive keyword stuffing or using irrelevant descriptions may be seen as Keyword Stuffing, which may lead to search engine penalties. The ideal practice is to make the alt text both concise and descriptive, accurately reflecting the image's content while aligning with the page's theme and keywords.
(1) Technical implementation of alt text
Nowadays, whether it's a SaaS platform or a CMS system, alt text has become an essential basic feature. As shown in the red box in the image above, WordPress allows users to directly input alt text after clicking on a media file in the media library. This feature makes adding image descriptions simple and quick without the need for additional programming.
12、Website Structure (Navigation Menus)
The website structure is generally directly reflected in the main navigation menu. The structure demonstration in the image above shows a website structure that complies with both user experience and SEO guidelines. A website structure that adheres to user experience and SEO standards typically has clear hierarchical relationships and logical organization, where each level is not isolated but is linked to its parent or child pages. If there is a page that stands alone without being connected to other levels or pages, this is referred to as an "orphan page," which does not comply with SEO standards. A well-designed website structure not only helps visitors quickly find the information they need but also improves search engine crawling efficiency, thus improving the site's rankings. The design of the main navigation should be organized based on the core content of the website, typically consisting of primary and secondary menus. The primary menu represents the main content categories, while the secondary menu further details specific content or services. This way, website visitors can easily understand the relationship between different sections and quickly find the pages they need.
13. SEO-Related HTTP Status Codes
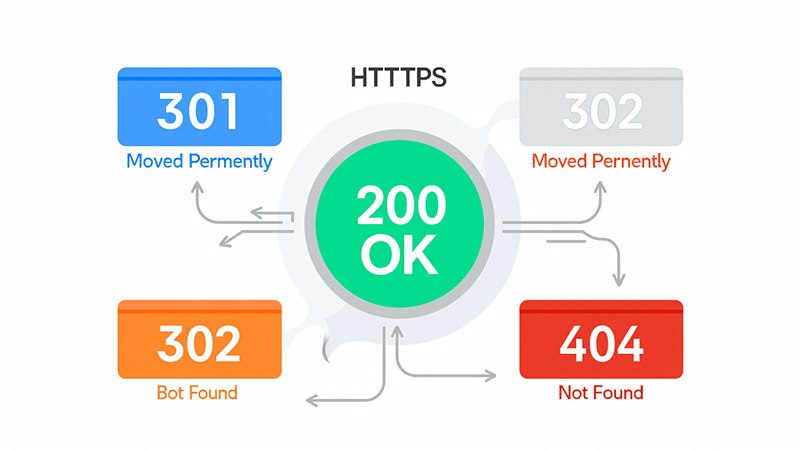
In SEO, HTTP status codes refer to the status information returned by the server when responding to a request. These status codes help search engines understand the status of a page, which in turn influences whether the page will be crawled, indexed, or ranked. Understanding different HTTP status codes and their impact on SEO is crucial. By correctly using 301 and 302 redirects, avoiding errors like 404 and 500, and optimizing server response times, a site can offer a better user experience and help search engines crawl and rank pages. Below are common SEO-related status codes and their descriptions:
(1)200 OK
The 200 status code indicates a successful request, with the server returning the requested page content. This is a very common status code, meaning the page is accessible and valid. For SEO, a page returning a 200 status code means it is functioning properly and will be crawled and indexed by search engines.
(2)301 Moved Permanently
The 301 status code indicates that a page has been permanently moved to a new location. When the URL of a page changes or is redirected to a new page, a 301 redirect informs search engines that the page has permanently migrated. This status code is important for SEO because it passes most of the original page’s weight (i.e., page rank and link value) to the new URL, helping to maintain search engine rankings.
(3)302 Found (Temporary Redirect)
The 302 status code indicates that the page is temporarily redirected to another URL. Unlike the 301 redirect, the 302 redirect suggests that the page is temporarily moved, and search engines should continue to crawl the original URL rather than the new one. SEO-wise, 302 redirects do not pass all SEO weight to the target page, so if the redirection is permanent, 301 should be used instead.
(4)404 Not Found
The 404 status code indicates that the server could not find the requested page. This usually means the page has been deleted or the URL is incorrect. In SEO, a 404 page can affect user experience and search engine rankings. To avoid negative SEO effects from 404 pages, you can set up 301 redirects or create a custom 404 page to guide users.
(5)410 Gone
The 410 status code indicates that the page has been permanently deleted and will no longer return. Unlike the 404 error, the 410 status code clearly tells search engines that the page is no longer valid and should be removed from the index. For SEO, the 410 status is more beneficial than 404 when a page is permanently removed.
(6)500 Internal Server Error
The 500 status code indicates an internal server error that prevents the server from completing the request. When this error occurs, search engines cannot access the page, which can negatively affect SEO. If this error persists, search engines may remove the page from the index, so it’s crucial to fix server issues promptly.
(7)502 Bad Gateway
The 502 status code indicates that the server, acting as a gateway or proxy, received an invalid response from the upstream server. Similar to the 500 error, a 502 error means the server is not functioning correctly, which may prevent search engines from accessing the page. If this error persists, it can impact the website's SEO performance.
(8)503 Service Unavailable
The 503 status code indicates that the server is temporarily unable to handle the request, usually due to server overload or maintenance. This is a temporary error, and search engines typically retry the request later. However, if the 503 error occurs frequently, it can affect the page's crawling and ranking.
(9)504 Gateway Timeout
The 504 status code indicates that the server, acting as a gateway or proxy, did not receive a response from the upstream server within the allotted time. Similar to the 502 error, the 504 status suggests a server issue that may affect crawling. When this error occurs, search engines will pause access to the page until the server is back online.
(10)Status Code Detection and Validation
Method 1: Use Status Code Detection Tools
The image above shows the Status Code Detection Tool developed by Logic Digital Technology. You can directly input the page's URL and click the "Query" button on the right to view the status code returned by the page in the query result area below. The entry path to the status code detection tool can be found in the navigation menu of Logic Digital Technology's official website under "Tools" - "Page Status Code Query."
Method 2: Detect status code in the browser's developer mode
In the browser’s developer mode, select the "Network" tab. Then, either enter the URL of the page you want to check in the URL input bar, or if you’ve already visited the page, simply press the Enter key again to reconnect and re-download the page's files. Once the page files are loaded under the "Network" section, find the document corresponding to the page URL, and you will see the recorded page status code in the "Status" header on the right side.
14、Submitting a Site to Search Engines
The specific process for Submitting a New Site to Search Engines has already been covered in a dedicated technical tutorial published by the blogger. You can directly visit and read the article "Submitting Your Website to Google, Baidu, Bing, and Yandex Search Engines" to follow the steps outlined in the article to submit your website to Google Search Engine. The article "Submitting Your Website to Google, Baidu, Bing, and Yandex Search Engines" not only covers the technical steps for submitting to Google, but also includes instructions for submitting to Baidu, Bing, and Yandex.
15、Checking the Number of Pages Indexed by Search Engines
The indexing volume of a search engine refers to the total number of specific pages from a website that the search engine has indexed. This value is commonly used to measure a website's page inclusion rate. Page inclusion rate is a key metric in SEO, directly reflecting a website's visibility and crawling status within search engines. The higher a website's page inclusion rate, the more thoroughly the search engine indexes its pages, which indicates better SEO performance. A higher page inclusion rate generally also means more opportunities for the website to rank on search engine results pages (SERPs), bringing more organic traffic. In addition to directly impacting the visibility of a website in search engines, page inclusion rate also indirectly affects the indexing and ranking performance of keywords. If a website's pages are widely indexed, search engines can better identify and match content related to specific keywords, thus increasing the ranking opportunities for those keywords. The higher the ranking, the more organic traffic it generates. Therefore, page inclusion rate is not only an important dimension for measuring SEO success, but it also largely determines the exposure and potential visitors a website can get through organic search traffic. To ensure ongoing SEO optimization, improving a website's page inclusion rate and visibility should be one of the core goals for every website administrator and SEO professional.
(1) Check the indexing of website pages in Google Search Console
Click "Web Pages" under the "Indexing" management tool in the left sidebar of Google Search Console to enter the data interface for page indexing statistics. In this interface, you can see the number of indexed pages and the number of non-indexed pages on the website and the reasons.
(2) Viewing Website Page Indexing in Bing Webmaster Tools
Enter the Webmaster Tools management backend, click on the "Site Manager" tool in the left sidebar, and in the content area on the right, you will see the information about the website being crawled, including the number of indexed pages.
16、Submitting New Pages or Updated Content

When we publish new pages or posts, or update the content of existing pages, it is crucial to submit these updates to search engines in a timely manner. Only by doing this can search engines quickly identify and crawl the new or updated content and present it in search results, ensuring that the website content is quickly discovered by users. Major search engines like Google and Bing provide specific functions that allow webmasters to submit the URLs of new or updated pages. This process is done through the respective search engine management backend, where we simply enter the page's URL into the designated submission box, and the search engine will begin crawling these pages. In this way, whether it is a newly published page or an old page that has been updated, it can be recognized and indexed by the search engine faster. It is important to note that the need to submit new pages and updated pages is essentially the same: both require URL submission to notify search engines. Therefore, by using this feature effectively, not only can the content update cycle be accelerated, but it also ensures that the website remains in the latest index of search engines, improving the visibility of pages in search results. This submission process is simple, but it is crucial for improving a website's SEO performance and ensuring that content is reflected in search engine results in a timely manner.
(1) Method to Submit New Pages or Updated Content to Google
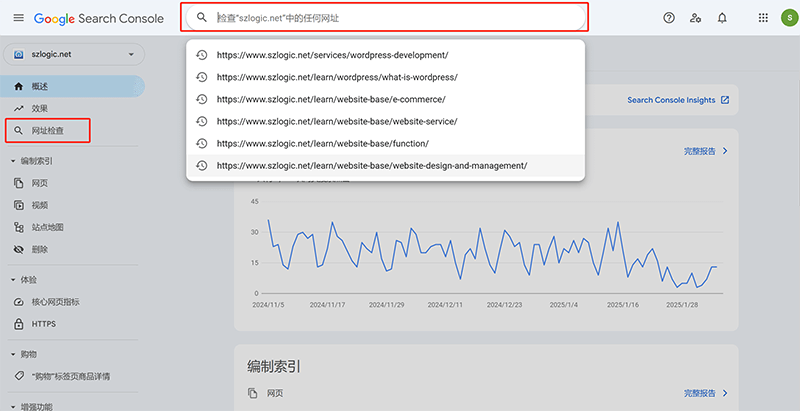
The specific operation for submitting new pages or updated content to Google is as follows: first, log in to Google Search Console, then click on "URL Inspection" in the left-hand toolbar, as shown in the red box in the image above. In the URL input box that appears at the top of the page (marked in the red box in the image above), enter the URL of the new page or the page with updated content. After entering the URL in the inspection interface, click the "Request Indexing" button.
(2) Method to Submit New Pages or Updated Content to Bing
The method to submit new pages or updated content to Bing is as follows, as indicated in the red box in the image above: Click on the "URL Inspection" tool in the left sidebar of the Bing Webmaster Tools dashboard. In the URL input box at the top of the operation area on the right (as shown in the red box in the image above), enter the URL of the new page or the page with updated content. After entering the URL, click the "Check" button on the right of the input box. In the updated interface, click the "Request Indexing" button, and a confirmation window will pop up. Click the "Submit" button in the window to confirm the operation.
Ⅲ、SEO Keyword Research

SEO keyword research is the foundation of optimization strategy, which is why it plays a crucial role in search engine optimization. It directly determines how well a website performs on search engine results pages. Through keyword research, SEO professionals can understand the actual terms users input into search engines, allowing them to develop more targeted optimization strategies for website content. Keyword research helps identify core conversion keywords or long-tail keywords that attract the target audience. These keywords not only increase a website’s visibility on search engines but also enhance its relevance and competitiveness.
Effective keyword research ensures that a website's content closely aligns with user search intent. When a webpage highly matches a user's query, search engines are more likely to rank it higher in the results, thereby bringing more organic traffic. In addition, through various keywords and industry trends, SEO keyword research can reveal potential opportunities and market gaps, helping a website stand out in a competitive environment. Keyword selection is not only about increasing traffic, but also about influencing conversion rates. By choosing keywords that meet user needs, demonstrate high search intent, and possess commercial value, a website can attract more targeted traffic. This type of traffic typically has higher conversion potential because the users’ search intentions are more specific. Therefore, keyword research is not merely aimed at boosting traffic but also at improving the quality and relevance of website content, ultimately achieving higher conversion rates and return on investment. Finally, it's important to note that keyword analysis and research do not differentiate between SEO Or SEM. The keywords used in both marketing models are interchangeable. In other words, as long as the keywords meet the criteria for search volume and commercial value, they can be included in the SEO keyword library and applied to SEO content, even if they were originally acquired through search engine advertising.
1、Types of Keywords
In the field of SEO, there has never been a unified standard for categorizing keyword types, which leads to some variations among different SEO practitioners. Based on the blogger's years of SEO practice, the blogger personally divides keywords into three main types: Root Keywords, Core Conversion Keywords, and Long-Tail Keywords. These three types of keywords each have distinct characteristics in terms of search volume and commercial value, and thus play different roles in SEO strategies.
2、Commercial Value and Search Volume Characteristics of Keywords
Root keywords are typically single words that represent core concepts within an industry or field. Due to their brevity and high level of abstraction, root keywords often have very high search volumes but also face intense competition. However, while these keywords can generate a large amount of traffic, they are usually quite broad and not well-aligned with users' specific needs, resulting in lower conversion rates. On the other hand, core conversion keywords are typically more specific and directly related to conversions. These keywords tend to accurately reflect users' purchase intent or action-driven behavior. Although their search volumes may not be as large as root keywords, their commercial value is relatively higher, as they attract more precise traffic with greater conversion potential. Long-tail keywords are longer phrases made up of multiple words. These have relatively lower search volumes but are highly targeted. Since long-tail keywords are usually more specific and align with users' particular needs, they can attract more precise traffic and face lower competition. Therefore, while each long-tail keyword may have a smaller search volume than root keywords, an effective long-tail keyword strategy can help a website accumulate significant overall traffic from multiple low-traffic keywords, while also increasing the conversion rate.
3、Keyword Search Volume Analysis
When conducting keyword analysis, analyzing search volume is a crucial step that should not be overlooked. The search volume of a keyword not only reflects its popularity but also directly impacts the amount of traffic that SEO can bring. The higher the search volume of a keyword, the greater the potential traffic. Therefore, understanding keyword search volume is essential for formulating effective SEO strategies. Taking Google Search Engine as an example, it offers an authoritative keyword analysis tool — Google Keyword Planner. Through this tool, users can enter relevant keywords and obtain key data such as the average monthly search volume, search volume trends over the past three months, and the level of keyword competition. This information helps SEO professionals understand keyword popularity, seasonal trends, and market competition, enabling them to make more targeted optimization decisions.
However, it is important to note that Google Keyword Planner is a tool within the Google Ads system, optimized primarily for advertising needs. Therefore, the competition data provided in the tool is related to ad competition, and may not accurately reflect the competition intensity for SEO purposes. This distinction is particularly important for SEO professionals, as the competition for ads differs from the competition for organic search rankings. Nonetheless, Google Keyword Planner remains a valuable tool, providing SEO with important data such as keyword search volume and trend analysis, which can help optimize content and improve a website's performance in search engines.
4、Keyword Competition Analysis

To analyze the competition level of keywords, we need to use professional third-party SEO data analysis tools. These tools provide in-depth market insights and competitive analysis capabilities. Personally, I prefer using Ahrefs' Keywords Explorer feature for keyword competition analysis (KD value). The KD value, highlighted in the red box in the image, is Ahrefs' feedback on the competition level of a keyword. The KD value is an indicator used by Ahrefs to measure the competitiveness of a keyword, ranging from 0 to 100. The higher the value, the more competitive the keyword is. Therefore, analyzing the KD value helps us quickly assess the difficulty of ranking for a keyword in search engines, allowing us to decide whether it is worth investing optimization resources. Keywords with a lower KD value are easier to optimize and may bring more accessible traffic to the website, while keywords with a higher KD value may require more optimization efforts and resources.
In addition, KD value analysis provides us with another level of insight: by understanding the competition difficulty of a keyword, we can reflect on our own content creation and link-building capabilities. Specifically, if we find that a keyword has a high KD value, and our current content quality or external backlinks are insufficient to compete with the top-ranking pages, we may need to adjust our strategy by enhancing content depth and authority or strengthening our backlink profile. The KD value is not just a simple number; it actually reflects our ability to effectively compete with competitors. Therefore, through Ahrefs' competition analysis, we can not only choose the right keywords for optimization but also gain strategic guidance for our SEO efforts.
5、Creating an SEO Keyword Database Table
| Types of Keywords | Keywords | Keyword Status | Monthly keyword searches | Keyword KD value | Keyword Theme URL | Average keyword ranking |
| Long tail keywords | seo guidance service | Arranged | 10 | 8 | https://www.szlogic.net/seo/ | 5 |
Ⅳ、SEO Content Planning
As shown in the content section planning diagram of LogicMind Technology from that year, the SEO content sections refer to the structured division of a website's content, typically consisting of primary category directories, which may then extend to multiple secondary categories. The design of primary categories usually has a clear directional focus and must be conceptualized based on the overall goals of the website and user needs, and integrated into the website's main navigation menu to ensure users can easily access each important content module. The setup of secondary categories is determined according to the specific needs of the website. For some websites, secondary categories may not require an actual directory within the site structure but instead serve as a thematic division of content. Structuring the content in this way helps both users and search engines better understand and navigate the site's categorized content.
For example, in the SEO content section planning of the “Logic Digital Technology” official website shown in the image above, the site's primary category directories include "SEO Techniques", "WordPress", "Google Tools", "Plugin Configuration", and "Website Fundamentals". These content categories form the foundational structure of the website's SEO content and are clearly presented in the main navigation. However, the approach to secondary categories is different. The blogger does not display these subcategories as actual directories in the navigation menu, but instead organizes the detailed content of the website by planning thematic content. This approach makes the site structure more flexible, avoids unnecessary directory levels, and still ensures that each topic is clearly segmented and presented.
When SEO managers are planning the content structure of a website, they must have a deep understanding of the site's products or services and its target audience. Only by fully grasping this information can they design a content structure that aligns with the website's business objectives while effectively meeting user needs. Understanding the core value of the products and services, as well as the interests, needs, and behavior patterns of the target audience, is key to ensuring that the content structure is consistent with the website's overall strategy. A clear and well-structured content section not only helps users quickly find the information they need, but also enhances the search engine's crawling efficiency, increasing the website's visibility and competitiveness. Therefore, SEO managers need to analyze the product characteristics, market positioning, and user habits from multiple dimensions to precisely plan the hierarchy and division of content sections. This approach ensures that the website's content architecture has commercial value while maximizing user experience and search engine friendliness. The blogger will now delve into how to plan SEO content sections for a website based on different dimensions and indicators, helping find the optimal balance between business goals and user needs, thereby improving the overall SEO performance and user conversion rate of the website.
1、Relevance to Website Business Categories
"The relevance of website business categories" is an important dimension in SEO content section planning, referring to the degree of alignment between the website's content sections and its main business or operational field. The core of this dimension is to ensure that the website's content sections are closely related to the website's core business and target audience, providing truly valuable content for users. When a website's content sections are highly relevant to its business categories, search engines are more likely to recognize the website's theme and expertise, thus offering better ranking opportunities.
For example, if a website focuses on selling electronic products, its content sections should be designed around relevant topics such as "electronics reviews," "buying guides," and "usage tips." These sections are highly aligned with the website's business category, helping attract users interested in electronic products while providing clear signals to search engines about the website's expertise and authority. On the other hand, if the website's content sections deviate from its core business category, such as designing a health lifestyle section for a site focused on selling electronics, it may attract some traffic but have limited SEO benefits. It could even lead to search engine misinterpretation, negatively impacting the website's overall ranking. Therefore, the relevance of the website's business category is not only a basic requirement for content section planning but also a key factor for SEO success.
2、Target Audience Needs
"Target audience needs" is a key dimension in SEO content section planning. It refers to designing content based on the interests, problems, and needs of the website's target audience. Understanding the needs of the target audience goes beyond collecting basic information; it involves deeply analyzing what value and solutions they are seeking when visiting the website. The core of this dimension is to accurately address the audience's needs by providing targeted and actionable content, thus enhancing the website's appeal and user engagement. When developing content sections, the needs of the target audience must be the starting point. For example, if a website's target users are general product consumers or business clients, they might be interested in how to improve product efficiency, how to choose the right products or services, or how to solve common problems in a specific field. Therefore, the website should create related sections around these needs, such as "Product Usage Guides," "Tips for Choosing the Right Product," "Industry Solution Recommendations," etc. By focusing on and responding to these needs, the website can attract more target users and increase user engagement and conversion rates.
At the same time, understanding the target audience's needs is crucial for optimizing website content structure and section division. If the content provided by the website does not directly address the core needs of the users, even with high traffic, the user engagement time and conversion rates may still be low. Therefore, understanding the specific needs of the target audience through market research, user feedback, and competitive analysis is fundamental to designing content sections. This dimension helps ensure that the content created by the website is not only relevant but also provides practical help and value to the audience, thus improving SEO effectiveness and long-term user satisfaction.
3、Commercial Value (Conversion Value)
"Commercial value (conversion value)" is a key metric in SEO content section planning, referring to the ability of content design and optimization to directly or indirectly drive the website toward achieving its business goals. Conversion value is typically closely related to the core business objectives of the website, such as selling products, generating leads, enhancing brand awareness, or increasing user registrations. In the process of content section planning, understanding how each section supports the business objectives is crucial because each section must not only meet user needs but also drive users to complete specific conversion actions. When considering commercial value, it is essential to evaluate how each content section attracts the right traffic, increases user engagement, and ultimately converts into business outcomes. For example, an e-commerce website’s content sections may focus on "product reviews," "promotions," or "customer case studies," which not only help users better understand the products but also encourage them to make purchases on the site, thus driving sales conversions. Another example is a B2B service website, which could attract potential clients by using sections like "industry reports," "solution showcases," or "client testimonials," thereby increasing opportunities for consultations and contract signings.
Therefore, the consideration of commercial value and conversion value is not only to increase website traffic but also to focus on whether this traffic can effectively convert into actual business revenue. By optimizing content structure, clearly defining the target audience, and designing pathways that guide user behavior, a website can ensure that its content not only helps increase brand exposure but also achieves real results at key conversion points. This metric helps everyone realize that optimizing website content is not just about rankings, but also about driving tangible business outcomes through precise content planning.
4、Sustainability of Subcategory Creation

"The sustainability of sub-column creation" is an important dimension in SEO content column planning, referring to whether a sub-column has the potential for long-term thematic creation throughout the ongoing content update and optimization process. This dimension emphasizes that sub-columns need to be not only attractive and relevant in the initial stage but also capable of continuously providing valuable content over time. Sustainability involves not just regular content updates, but more importantly, content diversity, depth, and the potential for long-term creation. When planning sub-columns, considering their sustainability means setting clear content directions and goals for the column, ensuring that it can consistently produce valuable content related to the theme in the future.
5、Content Creation Ability and Sustainability

"Evaluating the website's content creation ability for the column" is a key assessment metric in SEO content column planning. It focuses on whether the website has sufficient resources, expertise, and creation capabilities when creating and maintaining specific content columns. The core of this evaluation standard is to ensure that the website can reasonably plan the depth and quality of content based on its actual situation when establishing content columns. Assessing content creation ability involves not only considering the existing team's content creation level but also whether the website can continuously and consistently provide high-quality content for the column to meet the needs of both users and search engines. In practice, this standard requires website managers to fully understand their team's professional background, technical content creation abilities, and available resources. If a column requires a lot of industry expertise or technical support, and the website's team has limited capabilities in these areas, then it is necessary to consider supplementing with external resources during column planning, such as inviting industry experts or outsourcing writing. On the other hand, if the website itself has a strong content creation ability and an experienced team, more detailed and in-depth content can be added in the column planning, improving the column's professionalism and authority.
In addition, evaluating one's content creation ability also includes assessing the sustainability of long-term content production. The website must consider whether it has sufficient creative resources to regularly update and maintain column content while ensuring the quality remains unaffected. A sustainable content creation mechanism can help the website cope with columns that require frequent updates, preventing content quality decline or stagnation due to insufficient resources. Through this evaluation dimension, the website can design content columns that align with its content creation capabilities, ensuring continuity, professionalism, and quality during execution. This realistic self-assessment helps avoid setting unrealistic goals, ensuring that the column can effectively support the website's SEO objectives and maintain competitiveness in long-term operations.
Ⅴ、SEO Topic Strategy

When formulating an SEO Topic (Topic Refers To Subject) strategy, understanding and addressing the user’s search intent is the top priority. Users often search with clear needs or questions, and content creators must delve into these intents to ensure that the content they produce accurately responds to users’ expectations. This not only helps improve the page’s click-through rate and dwell time but also builds user trust, thereby enhancing the overall ranking of the website. After clarifying user intent, targeting keywords becomes the core part of the strategy. Choosing the right keywords requires a high degree of relevance to the topic, as well as meeting certain search volume standards. High-search-volume keywords are highly competitive but can drive more traffic, while long-tail keywords, though lower in volume, can precisely attract the target audience. Therefore, based on a balance between search volume and competitiveness, rationally allocating core keywords and long-tail keywords is a key step in achieving effective SEO optimization.
Gaining effective theme development insights is crucial for content planning, and it can be approached from multiple dimensions. First, by analyzing the pages ranking high in search results, one can gain insights into the content types and structures preferred by both users and search engines. Second, exploring niche topics is also an important way to expand content breadth. By delving deep into specific issues within a particular field, websites can cater to more specialized audience needs. Additionally, tracking popular trends and current events can help keep the content timely and relevant, attracting more immediate traffic. When determining specific themes or titles, the use of modifiers can enhance the content's appeal. Modifiers such as "best," "comprehensive guide," or "2025 latest" not only increase the click-through rate but also help the content stand out in search results. At the same time, performing a content gap analysis can identify areas of opportunity within the current content library. By filling these gaps, websites can effectively cover more keywords and user needs, thereby improving overall competitiveness.
1、Single or Multiple Topic Implementation
In SEO strategy, implementing topic-based or multi-topic content structures is an effective optimization method that can help websites gain better visibility and rankings in search engines. Topic-based content typically focuses on a core subject, providing a comprehensive and in-depth exploration around that theme. Due to its systematic and professional nature, this type of content is often recognized by search engines as high-quality content, which helps it gain an advantage in rankings for relevant keywords. As long as the topic structure is clear, the information is complete, and it meets user needs, it can usually achieve good rankings in a relatively short time, especially in terms of covering long-tail keywords and establishing authority in a specific field. In contrast, dual-topic (or multi-topic) content involves two or more related but relatively independent themes. While this structure helps cover a broader range of keywords and audiences, it may face some challenges in SEO rankings. Even if the content quality is high, keywords for the primary topic often rank quickly, while keywords for the secondary topics typically take longer to appear in search results. This is because search engines prioritize the main theme of the page when determining its core focus, and it may take a longer evaluation period to establish the authority and relevance of secondary topics.
Additionally, different types of topics also have varying ranking rules. Topic-based content, due to its focus and depth, better meets search engines' requirements for authority and comprehensiveness. It is ideal for creating "pillar content" or "authority pages," which can help improve the overall thematic relevance of the website. On the other hand, multi-topic content is more suitable for news websites, as it can attract a broader audience. However, it requires the use of internal linking, keyword optimization, and continuous updates to gradually improve the ranking of secondary topics.
2、Answering User Search Intent
Addressing user search intent is a core aspect of SEO strategy, as it directly determines whether the content meets user needs, which in turn affects search engine rankings. When users perform searches, they typically have a clear purpose, and these intents can be broadly categorized into three types: informational, navigational, and transactional. Informational intent refers to users wanting to find an answer to a question or learn more about a particular topic, such as "How to make pizza" or "Basic principles of SEO." Navigational intent indicates that users are trying to find a specific website or brand, like searching for "Amazon official website." Transactional intent reflects users' desire to make a purchase or take action, such as "Buy running shoes" or "Sign up for Netflix." To effectively address these different types of search intent, content creators need to think from the user's perspective and provide precise, valuable information. For informational intent, the content should be comprehensive, authoritative, and well-organized to ensure users can quickly find answers. For navigational intent, the content should highlight brand or website information to make it easy for users to identify and access. For transactional intent, the content should emphasize the benefits of products or services, along with a clear call-to-action to encourage conversions.
Additionally, analyzing the existing content on the search engine results page (SERP) is an important method for understanding user intent. Pages that rank highly typically reflect the search engine's preferred format for answering a particular keyword or query. By studying the structure, language style, and depth of information on these pages, you can better adjust your content strategy to ensure it both meets user needs and aligns with search engine preferences.
3、Targeting Keywords
In an SEO strategy, targeting the right keywords is a core step in improving website visibility and attracting targeted traffic. The choice of keywords not only determines whether the content can be effectively indexed by search engines but also directly influences whether users can find your page in search results. The process of targeting keywords begins with understanding the search behavior and needs of the target audience, ensuring that the selected keywords closely align with user intent. The chosen keywords should be highly relevant to the content topic and have a sufficient search volume to ensure that they can attract enough traffic.
Here, it is necessary to revisit the types of keywords mentioned above in the keyword research section. Keyword types include Root Keywords, Core Conversion Keywords, and Long-Tail Keywords. Root Keywords are usually the most basic terms within an industry or field, such as “SEO,” “Fitness,” or “Photography.” These types of words have high search volumes but are extremely competitive. Due to their broad scope, user intent may not be clear enough. Therefore, they are suitable as a foundation for content but should not be the sole focus of optimization. Core Conversion Keywords are more specific and are directly related to users’ purchase or action intent, such as “Google SEO Optimization” or Independent Website Development. These keywords have higher commercial value and can effectively drive conversions, making them ideal choices for keyword placement in content. Long-Tail Keywords consist of multi-word combinations that form specific phrases. Although the search volume of individual keywords is lower, they usually face less competition and can attract more targeted users—for example, Professional WordPress Development Company or How Much Does Independent Website Development Cost. These keywords are especially suitable for blog articles or topic-based content and help establish authority in specific niche areas. When selecting keywords, it is also essential to consider keyword competitiveness and commercial value. Keywords with high search volumes often come with high competition, so decisions should be made based on the website’s actual situation and optimization capability.
4、Topic Ideation Clues
(1) Get clues for topic development from pages ranked high in search results
When developing an SEO content strategy, gathering clues from pages that rank highly in search results is an efficient and practical approach. These pages typically achieve high rankings in search engines because they excel in content quality, keyword optimization, user experience, and page structure. Analyzing these pages can help us understand the current preferences of search engines and the actual needs of users, providing valuable insights for our own content creation. First, by observing the titles and meta descriptions of high-ranking pages, we can understand how they use keywords and attract clicks. These pages often embed core keywords precisely in the title while using compelling wording to improve click-through rates. Additionally, the page structure is another important aspect to take note of, such as the setting of tables of contents, paragraph distribution, and use of internal links. These elements reflect the organization logic and information hierarchy of the content. These details not only enhance the user's reading experience but also help search engines better understand the page content.
Further analyzing the content depth and coverage of these pages is also crucial. High-ranking pages typically provide a comprehensive and in-depth exploration of their topics, not only offering basic information but also addressing related subtopics or common questions, thereby fulfilling the multi-layered needs of users. This provides us with ideas for expanding the content's dimensions, increasing the coverage of related information, and enhancing the page's comprehensiveness and authority. In addition to the content itself, user interaction and signals are also important indicators of page performance. Observing elements such as the comment section, social shares, and backlinks can help identify which topics or angles resonate more with users. These user feedbacks not only help us adjust content direction but also reveal potential trending topics and content gaps that have not been fully covered.
Finally, by analyzing the performance of top-ranking pages, we can identify areas for content optimization and innovation. While learning from existing successful examples is effective, standing out in a competitive environment requires innovation in content depth, uniqueness, and user experience. By aligning with your brand’s characteristics and the needs of your target audience, creating differentiated and high-value content is the key to truly improving SEO performance.
(2) Tracking hot trends and current affairs topics
In SEO theme strategy development, tracking trending topics and current events is an important way to increase website traffic and user engagement. As user interests and social dynamics continue to evolve, search engines tend to prioritize content related to current hot topics. Therefore, capturing these trends in a timely manner and integrating them into content creation can significantly boost page visibility and rankings. There are multiple ways to discover trending topics. Tools such as Google Trends, Weibo Hot Search, and Twitter Trends can be used to stay up to date with global or region-specific trending topics. Additionally, industry-related forums, news websites, and professional blogs are also important channels for acquiring trend information. These platforms offer insights into which topics are generating widespread discussion and which keywords are experiencing a rapid increase in search volume. Constantly monitoring these changes helps in quickly creating and publishing relevant content as soon as a topic starts gaining traction, allowing you to seize a ranking advantage in search engines.
When a popular trend or current event overlaps with your website’s products or services, it’s crucial to seize the opportunity and create relevant topic content promptly. For example, if your website specializes in health products and a new health diet trend is becoming popular, you could write articles around this diet, discussing its principles, pros and cons, and how it relates to your products. Such content not only attracts users interested in the topic but also helps convert them into potential customers. Moreover, updating content based on current hot topics makes your website appear timely and authoritative, boosting users' trust in your brand. When creating content related to trending topics, it’s important not only to act quickly but also to ensure depth and quality. Simple content stacking won’t stand out in a competitive environment. Offering in-depth analysis, unique insights, and practical advice is what truly grabs users’ attention and helps secure higher search rankings. Additionally, optimizing with appropriate keywords to ensure the content is quickly crawled and indexed by search engines is key to improving rankings.
(3) Mining niche topics
In SEO topic strategy, exploring niche topics is an effective way to boost website traffic and rankings. Compared to broad popular topics, niche topics often focus on the needs of specific fields or user groups. While the search volume may be smaller, the competition is also relatively lower, making it easier to gain favor from search engines. By delving into these niche areas, websites can meet users' precise needs, enhancing authority and user engagement. The key to uncovering niche topics lies in understanding users' real needs and pain points. A common method is to analyze frequently asked questions (FAQs), forums, and comment sections. These platforms often gather significant user feedback and concerns. By systematically reviewing these questions, many underexplored or unanswered detailed topics can be identified. For instance, on specialized technical forums, users might discuss tips for using specific features or issues they've encountered—details that are often overlooked in mainstream content. By distilling these user-driven issues into targeted content, websites can attract more precise traffic and effectively reduce keyword competition.
Another important approach is to use keyword research tools like Ahrefs or Semrush to uncover long-tail keywords related to core topics. These long-tail keywords often point to more specific, refined content needs. For example, if the core topic is "SEO optimization," a niche topic could be "how to optimize image SEO" or "best SEO tools for beginners." By systematically analyzing the search volume and competition level of these long-tail keywords, you can identify niche topics that have traffic potential without being overly competitive. In addition to drawing inspiration from user feedback and keyword tools, industry trends and new technological developments also provide a rich source of material for discovering niche topics. As industries evolve, new problems and needs continuously emerge. Capturing these changes in a timely manner can help a website maintain its content's relevance and uniqueness. For instance, in the tech field, after the release of a new device or software, users often look for specific usage guides or reviews—these are niche topics that can be quickly tapped into.
5、Choosing Modifiers for Topics (Titles)
In SEO theme strategy, selecting the right modifiers for topics (titles) plays a crucial role in attracting user clicks and improving page rankings. An attention-grabbing title not only clearly conveys the core value of the content but also stimulates user interest, thereby increasing the click-through rate (CTR), which is one of the key metrics search engines use to measure page relevance and popularity. The appropriate use of modifiers can make a title more appealing, highlighting the uniqueness and practicality of the content, helping the page gain more clicks when it appears in front of users. The choice of modifiers should be based on users' search intent and psychological needs. For example, when users are seeking information, they are often attracted to words that directly meet their needs or solve problems, such as "fast," "simple," or "comprehensive." Meanwhile, when comparing products or services, terms like "best," "recommended," or "cost-effective" are more enticing. Depending on the type of content and user needs, the following common modifiers can be flexibly used:
(1) Modifiers for topics (titles) that emphasize practicality and efficiency:
Fast, simple, convenient, practical, efficient, step-by-step.
(2) Modifiers for topics (titles) that emphasize authority and comprehensiveness:
Complete, comprehensive, in-depth, authoritative, ultimate guide, detailed explanation.
(3) Modifiers for topics (titles) that guide user decision-making:
Best, recommended, popular, selected, must-see, first choice.
(4) Modifiers for topics (titles) that stimulate curiosity and urgency:
Amazing, unbelievable, things you don’t know, latest, limited-time, now.
(5) Modifiers for topics (titles) that emphasize comparison and evaluation:
Comparison, review, differences, pros and cons, ranking, cost-effectiveness.
(6) Modifiers for topics (titles) aimed at specific groups or needs:
Beginner-friendly, expert guide, must-read for newbies, business use, personal use.
(7) Modifiers for topics (titles) that emphasize results and outcomes:
Enhance, increase, improve, solve, save, achieve goals.
For example, when writing content related to “general consumer goods,” you can use modifiers to make the title more appealing, such as "Quick Start Tips for Home Coffee Machines" or "Comprehensive Skincare Guide for Beginners." These modifiers not only help users quickly assess the value of the content but also spark their interest to click, thus improving the page's performance in search engines.
6、Material (Media Files) Production
A well-crafted SEO piece is always rich in elements and has a well-structured design. An indispensable part of this is the materials (media files) used within the article. These materials can include high-definition images, infographics, embedded videos, GIFs, or even audio clips. Properly integrating these media files into the content not only enriches the page's visual elements but also enhances overall readability, making the reading experience more enjoyable and helping to avoid reader fatigue caused by plain text content. Additionally, appropriate media can provide more intuitive explanations of complex concepts, improving the efficiency and accuracy of information delivery, and increasing user dwell time, which indirectly boosts the page's SEO performance. However, these media files should not be added haphazardly at the final stages of content creation. Instead, they should be carefully planned during the SEO topic strategy formulation phase. Specifically, early in the SEO strategy development process, the required types and number of media files for each piece of content should be clearly defined, and a detailed media list should be created. This list should include specific image descriptions, video themes, chart design needs, etc., which will then be handled by professional designers or video production and editing personnel. This way, when SEO editors begin writing and publishing content, the required media files are already prepared and can be inserted in the appropriate places, ensuring that the publishing process is not delayed due to missing media.
The standardization and advance planning of this process can significantly improve content production efficiency and ensure that the overall style and visual elements of the article align with the SEO theme. Moreover, high-quality original media files can enhance the uniqueness of the page, avoiding issues of content duplication caused by the excessive use of publicly available online materials. This, in turn, helps improve the search engine friendliness and page ranking. Therefore, in SEO topic strategy formulation, the production and planning of materials (media files) is a crucial step that affects both content quality and publishing efficiency, and it should never be overlooked.
7、Content Gap Analysis
Content gap analysis is a crucial step in SEO theme strategy formulation, aimed at identifying the differences in content between your own website and competitors, in order to optimize strategies and improve ranking performance. When conducting the analysis, you should first search for the target keywords on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) and observe the types of pages that rank highly. These pages may be Topic-Focused Content centered around a single subject, often characterized by high focus and well-structured layouts, making them more likely to achieve better rankings. They may also be Dual-Topic or multi-topic pages. Although such content can be of high quality, keywords related to subtopics often take longer to achieve notable rankings. This requires us to clearly define the thematic focus when creating content and avoid information dispersion. Next, pay attention to the Relevance of the content to the theme. Search engines favor content that closely matches the user's search intent. Therefore, analyzing the thematic coverage and depth of high-ranking pages can help determine whether we need to adjust the focus of our own content or supplement missing areas. If competitor pages offer more in-depth and comprehensive answers while our existing content provides only a superficial overview, then our optimization direction should focus on enhancing the depth and detail of our content.
Content Structure is also an important factor influencing SEO performance. High-ranking pages typically use a clear hierarchical structure, making effective use of H1, H2, H3, and other heading tags to help both readers and search engines quickly understand how the information is organized. In addition, the Composition Of Page Elements also deserves attention. Excellent pages are not composed of plain text alone; they also integrate multimedia elements such as images, videos, infographics, and cited data to enhance content richness and user experience. In contrast, if your own content lacks diverse media support, it’s necessary to supplement and optimize in this area. Content Length And Depth is another key consideration. Generally, search engines prefer long-form content that covers a wide scope and provides detailed information. However, this doesn’t mean all content should pursue maximum word count. The ideal length should be determined based on the complexity of the topic and user needs, ensuring the topic is comprehensively covered without becoming unnecessarily lengthy. Thoroughly exploring details and offering practical information can effectively boost the authority of the content and increase user engagement.
Finally, the Number And Quality Of Backlinks directly affects the authority and ranking of a page. By analyzing the backlink profile of competitors' pages, you can assess your own shortcomings in link building. If competing pages have a large number of high-quality backlinks while your own pages fall short in this area, it's essential to take action to increase the number of quality backlinks. This can include content collaborations, obtaining recommendations from authoritative websites within the industry, or promoting content through social media to attract organic links. Analyzing from these dimensions can help us fully understand our content’s position in the SEO landscape, identify areas for improvement, and develop more targeted optimization strategies, ultimately achieving better performance in search engine results.
Ⅵ、SEO Content Quality Evaluation Metrics
1、Keyword Placement
In SEO content optimization, keyword placement is a core step in improving a page's ranking in search engines. The selection and arrangement of keywords should be based on the specific content strategy and goals. Typically, a combination of 1-2 types of keywords is chosen as the optimization focus, such as root keywords + long-tail keywords or core conversion keywords + long-tail keywords, rather than applying all three types of keywords to the same content. After selecting the keyword types, they should be placed according to SEO rules. Once the keyword types are determined, the placement of the keywords is crucial. The most important positions are the title tag and H1 header, as search engines prioritize these areas to determine the core theme of the page. For example, if the root keyword is "running shoes," the title could be set as "Professional Running Shoes Buying Guide," and the H1 could directly use "Running Shoes Buying Tips" to ensure the theme is clear, concise, and prominent.
If the core conversion keyword is chosen, such as "lightweight running shoes purchase," it should also be placed in both the H1 and title tags. For example, "Lightweight Running Shoes Buying Guide: How to Choose the Right Pair" and "Best Styles for Lightweight Running Shoes Purchase" can be placed in the H1 and title tags respectively. These types of keywords are more commercially driven and can effectively guide users toward conversion. In the body content, long-tail keywords like "recommended running shoes for marathon beginners" can be placed in subheadings (H2, H3) to further enhance the number and relevance of keyword placements on the page. These long-tail keywords have lower competition but can precisely match user search intent, helping to improve the page's ranking for specific searches.
2、Topic Relevance
Topic Relevance is one of the core metrics in SEO content optimization. It refers to the degree to which a webpage’s content matches the user's search intent and keywords. Highly relevant content can better meet user needs and improve the page’s ranking in search engine results. When ensuring topic relevance, the proper use of the H1-Hn Heading structure is especially important, as these headings not only help readers quickly understand the content hierarchy but also provide clear signals to search engines about the page’s topic.
First, the H1 Tag serves as the main title of the page. It should be used only once and must directly reflect the core topic of the page. The H1 should include the most important keyword to ensure that search engines can accurately identify the page content. For example, if your topic is "Fat Loss Diet," an appropriate H1 could be "A Comprehensive Guide to Fat Loss Diets"—this clearly states the topic and incorporates the core keyword. Next are the H2-Hn Subheadings. These subheadings are used to organize the content structure and should further elaborate on the topic while maintaining a high degree of relevance to the H1 heading. The H2 tags divide major sections, while H3 and lower-level headings are used for more detailed subsections. For example:
- H2: Food types suitable for fat loss
- H3: High-protein food recommendations
- H3: Low-Carbohydrate Food Choices
- H2: Dietary Misconceptions During Fat Loss
- H3: Risks of Ignoring Caloric Intake
- H3: The impact of excessive dieting on the body
The main content should be developed around these headings, ensuring that each section remains closely aligned with the subheadings and main title, without deviating from the topic. When inserting relevant images, charts, or videos, their descriptions and the ALT Tag should also align with the page’s theme to further enhance topical relevance. Optimizing Topical Relevance is not simply about keyword stuffing; it involves using a logical heading hierarchy, content depth, and multimedia elements to keep the entire article consistently focused on the core theme, thereby improving SEO performance.
3、Structural Standards
Structural Consistency is a vital component of SEO content optimization. It refers to the logical organization of webpage content in terms of heading hierarchy and formatting. A well-structured layout not only enhances the reading experience for users but also helps search engines better understand and index the page content, thereby improving rankings. In SEO, the correct use and hierarchical relationship of H1 through H6 tags are crucial, as they collectively form the framework of the webpage’s content.
First, the H1 Tag is the main title of the page and should only be used once to directly reflect the core theme of the page. The H1 tag should be placed at the very top of the page and clearly state the main content of the article or webpage. For example, if the page is a guide on "How to Improve Website Speed," the H1 could be set as "The Complete Guide to Improving Website Speed." Next, the H2 Tag is used to divide the page into main sections or chapters. Each H2 title should be a subtopic of the H1 theme, helping to refine and complement the main title. For example, in the above case, H2 titles could include "Main Factors Affecting Website Speed" and "Methods for Optimizing Website Load Time."
The H3 Tag is used to further subdivide content under the H2, typically to list detailed steps, subtopics, or additional information. H3 should always maintain a logical subordination to its parent H2. For example, under "H2: Methods for Optimizing Website Load Time," there could be "H3: Compressing Image File Sizes" and "H3: Reducing HTTP Requests" as subheadings. Similarly, H4 to H6 Tags are used for even finer content divisions, but in general web content, using H4 is sufficient. H5 and H6 are typically used in more complex documents or technical documentation. It's important to note that these tags should follow a strict hierarchical order and should not be used out of sequence. For example, an H5 tag should not appear directly under an H3 tag; they must be nested in order.
A structured example is as follows:
- H1: Complete Guide to Improving Website Speed
- H2: Key Factors Affecting Website Speed
- H3: Server Response Time
- H3: Image and Multimedia File Size
- H2: Methods to Optimize Website Load Time
- H3: Using Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
- H4: Choosing the Right CDN Provider
- H3: Using Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
- H3: Minimizing CSS and JavaScript Files
- H2: Key Factors Affecting Website Speed
Through this clear hierarchical structure, not only can the logical flow and clarity of the user's browsing experience be enhanced, but it also makes it easier for search engines to crawl the page content, improving SEO rankings. The core of Structural Norms is to ensure the content is well-organized, avoiding the arbitrary use of heading tags or keyword stuffing, in order to achieve better content creation quality.
4、Content Depth and Length
Content depth and length are important indicators of SEO content quality, directly influencing a webpage's ranking performance in search engines. High-quality content not only needs to cover sufficient breadth and detail but also requires a well-structured hierarchy to ensure that both users and search engines can easily access key information.
(1) Content Depth
Content depth refers to the level of detail covered in the content, often reflected in the use of heading tags from H1 to H6. In SEO optimization, appropriately utilizing heading tags can effectively enhance content depth. In practice, content depth and length should complement each other. Depth determines the professionalism of the content and user engagement, while length ensures sufficient information density and keyword coverage. When writing SEO content, it's essential to maintain a clear structure with a logical hierarchy, while also adjusting word count according to the topic requirements to provide enough information to meet both user and search engine needs.
- H1: Used as the core title of the page, summarizing the main theme of the entire content. It can only be used once per page to ensure the theme is clear.
- H2: Used to divide the main sections of the content, further elaborating on the core content of the H1 title. Each H2 represents an important subtopic of the article.
- H3: Further breaks down specific content under H2, suitable for listing details, steps, or subtopics.
- H4-H6: Used for more complex or hierarchical content structures, typically in technical or in-depth analysis articles (for example, H6 is used in some of the chapters in this article). These tags help present more detailed content, but should not be overused to avoid negatively impacting the reading experience.
Generally speaking, regular SEO articles typically use H3 to meet most needs. However, when displaying in-depth analysis or complex logic, it can extend to H4 or even H5, but always maintain logical consistency in the heading hierarchy.
(2) Content length
Content length focuses on the word count and overall length of the content. In SEO, the length of the content should be determined by the complexity of the topic and the needs of the target audience.
- Short Content (1000-2000 words): Suitable for news briefs, simple tutorials, or product introductions. This type of content goes straight to the point, quickly conveying key information. However, in highly competitive keyword fields, it may be difficult to achieve a high ranking.
- Medium-Length Content (2000-10000 words): Suitable for basic guides or topic overviews, covering the main points while maintaining both depth and readability. This is the ideal length for most SEO articles.
- Long-Form Content (10000+ words): Ideal for comprehensive guides, in-depth analysis, or professional field content. These articles showcase expertise and authority, cover more long-tail keywords, and increase the page's weight in search engines.
5、Content Elements
Content composition elements are one of the key indicators for evaluating SEO content quality. Rich page elements not only enhance user experience but also improve the readability and ranking of the page in search engines. Text-only content can easily cause reader fatigue, while diverse elements can effectively capture attention, increase page dwell time, and have a positive impact on SEO. In practical creation, content composition elements typically include several major categories. By properly integrating these elements, you can not only enrich the presentation of the article but also enhance the user reading experience and interaction, ultimately boosting the page's search engine ranking. When creating SEO content, it's essential to flexibly use these elements according to the topic and audience needs, ensuring that the content is both informative and attractive. Details of different types of article page elements are as follows:
- Images and Videos: High-quality images and videos can visually convey information, help explain complex concepts, and enhance the visual appeal of content. For example, in tutorial or product introduction articles, pairing screenshots or demonstration videos can significantly improve the comprehensibility of the content. To optimize SEO, all images should include alt text, and videos can provide brief captions to help search engines understand the media content.
- Tables: Tables are useful for displaying comparative data, specifications, or process steps, presenting complex information in a clear and concise manner. Tables not only make it easier for users to reference, but also improve the page's structured data, helping it appear as rich snippets in search results, thereby enhancing the click-through rate.
- List Elements: Using ordered (numbered) or unordered (bulleted) lists can clearly present points, making it especially suitable for step-by-step guides, key point summaries, or product feature introductions. The list structure allows readers to quickly access key information and helps search engines identify the focus of the page, improving readability and ranking.
6、Number of Anchor Texts
The number of anchor texts is an important metric in evaluating SEO content quality, and it directly influences a page's ranking in search engine results. Anchor text refers to the text content that is embedded with a link, usually pointing to other pages within the same website (internal links) or to external websites (outbound links). A proper and reasonable amount of anchor text not only helps improve the site's structure but also enhances user experience and the page's authority. In SEO optimization, the role of anchor text is reflected in the following aspects:
(1) Enhancing Website Structure and Page Weight Transfer
Anchor text in internal links helps build the logical structure of the website, making it more efficient for search engines to crawl and index the site's content. By passing weight to important pages through anchor text, it helps improve their ranking in search results.
(2) Improving User Experience and Page Dwell Time
Properly distributed anchor text can guide users to deeper related content, increasing the depth and time spent on the site. This behavioral signal is seen by search engines as positive feedback on page quality, helping to improve overall ranking.
(3) Optimizing Keyword Rankings
Using appropriate keywords in anchor text helps search engines understand the topic of the linked page, improving its ranking for relevant keyword queries. However, overusing exact match keyword anchor text may be seen by search engines as over-optimization, leading to negative effects.
(4) Preventing Over-Optimization and Link Stuffing
While anchor text is beneficial for SEO, the quantity and distribution need to be reasonable. Excessive anchor text can negatively affect user reading experience and may be considered by search engines as link stuffing, which can reduce the page's authority. Therefore, it's advised to maintain a natural distribution of anchor text, ensuring that each link is closely related to its context.
It's important to note that optimizing the number of anchor texts requires balance. You need to ensure the rational distribution of internal links and the natural embedding of keywords while avoiding over-optimization that could negatively impact rankings. By following search engine SEO guidelines for anchor text usage, you can effectively improve page visibility and authority in search engine results.
7、Page Size Standards
According to Google's official documentation, Googlebot prioritizes processing the first 15 MB of content in each supported HTML or text file when crawling a webpage. Any content beyond this limit will not be crawled or indexed by Googlebot, meaning that any content beyond 15 MB will not appear in search engine indexes, which will affect the page's visibility and ranking performance. Therefore, to ensure that key content on the webpage is successfully crawled and indexed, it is important to strictly control the file size during the design and content creation process to ensure that the total page size does not exceed 15 MB. Additionally, the importance of content ordering is also crucial. Try to place core information, main keywords, and key media elements (such as images, videos, or important internal links) toward the beginning of the HTML file, ensuring that this content can still be successfully crawled by search engines even when approaching the file size limit. For larger image or video files, it is recommended to use external hosting services and link to them or use image compression, lazy loading, and other techniques to reduce file size, optimizing loading speed and crawling efficiency.
(1) Page volume detection method
As shown in the image above, after entering the browser's developer mode, select the "Network" tab in the top-right corner of the developer tools. Then, enter the page URL in the address bar and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Once the article page content is displayed, scroll to the bottom of the page using the mouse scroll wheel to view the total page size. In the image above, the 10.5MB indicated in the red box at the bottom of the browser's developer tools is the detected page size.
Ⅶ、Ranking Signals for Page Improvement
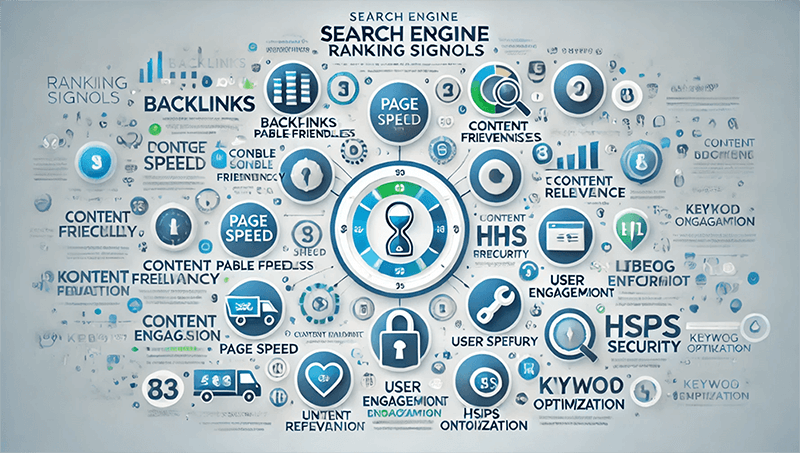
1、Natural Ranking Signals
Natural ranking signals refer to factors that improve a website's search engine ranking through high-quality content and excellent user experience, without relying on backlinks. These signals primarily focus on user interaction data, reflecting how appealing the page content is and how well it meets search demands. Here are several core natural ranking signals:
(1) Dwell Time
Dwell time refers to the amount of time a user spends on a webpage after clicking a search result, before returning to the search results page. A longer dwell time typically means that the user found valuable information on the page, with content that is engaging and thorough, effectively meeting their search needs. Search engines view this signal as positive feedback on page quality, which can improve rankings.
(2) Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is the percentage of users who leave a page without taking any further actions (such as clicking links or browsing other pages). A high bounce rate may indicate that the page content does not align with the user's search intent, or the page experience is poor. A low bounce rate usually suggests that users are interested in the content, thereby enhancing the page’s authority and ranking.
(3) Bookmarking
Users adding a page to their bookmarks or favorites may not directly affect rankings in traditional SEO, but in certain cases (such as Google Discover), search engines may record this behavior. Bookmarking typically reflects the value and reference-worthiness of the content, contributing to long-term organic traffic growth.
(4) Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR is the ratio of users who click on a page after it appears in search results. A higher CTR indicates that the page title and description are attractive to users and highly relevant to the search keywords. Search engines use CTR to assess the popularity of content, which can affect rankings. Optimizing titles and meta descriptions to increase CTR is an important method to improve natural rankings.
(5) Page Interaction Elements (such as Comments and Shares)
Interactive elements on a page, such as user comments, likes, and shares, increase the page's activity. These interactions not only extend the user’s time on the page but also broaden the content’s reach. Search engines may interpret high interaction volumes as a sign of page popularity and authority, which can help improve rankings. Additionally, social shares, while not directly affecting SEO, can increase page visibility and traffic, indirectly boosting natural rankings.
Natural ranking signals emphasize improving content quality and user experience to attract users to interact with the page, thus improving rankings without relying on backlinks. Focusing on user behavior data such as dwell time, bounce rate, and CTR, combined with rich interactive elements, can effectively enhance a webpage’s natural ranking in search engine results.
2、Backlinks (Inbound Links) Ranking Signals
Backlinks are one of the core factors in search engine ranking algorithms, directly reflecting how other websites recognize and recommend your content. High-quality backlinks can significantly enhance a website's authority and credibility, thereby improving its ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). Backlinks are not just about quantity; their quality, diversity of sources, and the sustainability of growth are even more important.
(1) Quality and Quantity of Referring Domains
Referring Domains refer to the number and quality of different external websites that link to your site. This metric is more important than simply the number of backlinks because links from multiple high-authority websites carry more weight than multiple links from a single low-quality site. Search engines prioritize links from authoritative sources such as industry-leading websites, news organizations, government sites, or educational institutions, as these are generally considered more trustworthy. Below are methods to improve the quality and quantity of referring domains:
- Acquiring High-Quality Links: Seek high-authority websites that are relevant to your website’s content. Try to acquire backlinks through content collaborations, guest blogging, or press releases.
- Diversifying Link Sources: Avoid links coming from a single or similar websites. Maintain diversity in your link sources to increase the trust search engines place on your website.
- Avoiding Low-Quality or Spammy Links: Search engines penalize low-quality links acquired through link farms or black-hat SEO tactics. Regularly use tools to check and clean these links.
(2) Sustained growth of external links (if the number of links is surpassed under the same content quality, the ranking will be surpassed)
Sustainability Of Backlink Growth refers to the speed and consistency at which a website acquires backlinks. Search engines prefer a natural and steadily growing link profile rather than a sudden spike in backlinks, which may be flagged as suspicious SEO practices. On the other hand, if the number of backlinks to a page is surpassed by competitors—assuming content quality is equal—it may lead to a drop in rankings, as search engines perceive a decline in the site's authority. Below are methods to maintain sustainable backlink growth:
- Regularly Publish High-Quality Content: Continuously provide valuable content for your audience, naturally attracting external website links.
- Promote Content: Promote your content through social media, email marketing, or industry forums to increase the chances of being cited.
- Monitor Competitors’ Backlink Growth: Use SEO tools to monitor competitors’ backlink strategies. Adjust your own backlink acquisition plans in real time to maintain an edge in the competition.
Backlink (Inbound Link) Ranking Signals play a crucial role in SEO, directly impacting a website's authority and search ranking. By Improving The Quality And Quantity Of Referring Domains and maintaining the Sustainability Of External Link Growth, you can effectively enhance your website’s performance in search engines. SEO optimization should focus on acquiring natural and high-quality backlinks while avoiding a large number of low-quality links in a short period, in order to maintain a stable ranking advantage over the long term.
3、Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR) Ranking Signals
Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR) are key indicators that measure the authority and credibility of a website as a whole and individual pages in search engines. These ratings are primarily determined by factors such as the quality and quantity of external links, as well as the internal linking structure, and they directly impact the ranking performance of the website and pages in search results. Understanding and optimizing DR and UR is one of the core strategies for improving SEO performance.
(1) Domain Rating (DR)
Domain Rating (DR) Reflects The Overall Authority Of A Website In Search Engines. It measures the quality and quantity of external links (backlinks) pointing to the website, as well as the authority of the referring websites. DR is typically represented by a score from 0 to 100, with a higher score indicating greater credibility and influence in the eyes of search engines. Websites with a high DR are more likely to achieve higher rankings for competitive keywords. Methods for increasing domain rating include:
- Acquire backlinks from high-authority websites, such as industry-leading sites, news media, government, or educational institution websites.
- Maintain diversity in backlinks to avoid reliance on a single source of links.
- Regularly check and fix broken backlinks to ensure link quality.
(2) Page Authority (UR, URL Rating)
Page Rating Focuses On The Authority And Ranking Potential Of A Single Web Page. UR (URL Rating) Is Also Calculated Based On The Quality And Quantity Of Backlinks, But It Only Considers The Link Profile Of A Specific URL. A Page With A High UR Typically Indicates High Content Quality And Recognition From Other Websites, Making It More Likely To Rank Well For Specific Keywords. Methods For Increasing Page Rating Include:
- Acquire high-quality backlinks for important pages, especially contextually relevant links.
- Use an internal linking strategy to pass authority from other high-authority pages on the website to the target page.
- Update and optimize page content to maintain freshness and relevance, attracting more natural backlinks.
(3) The relationship between domain authority (DR) and page authority (UR)
Although DR And UR Are Both Metrics Used To Measure Website Authority, They Serve Different Purposes And Emphasize Different Aspects. DR Focuses On The Overall Influence Of The Website, Providing A Weighted Impact Across All Pages Under The Same Domain. In Contrast, UR Focuses On Specific Pages. Even If A Website Has A High DR, A Particular Page May Still Have A Low UR If It Lacks Sufficient Backlink Support, Which Can Negatively Affect That Page’s Ranking.
- High DR + High UR: These pages typically have a high level of competitiveness in search engines and can rank well for popular keywords.
- High DR + Low UR: This indicates that the website has strong authority overall, but the specific page might lack backlinks or content quality, requiring further optimization.
- Low DR + High UR: These are typically pages on new websites that have gained good page weight through excellent content or backlinks, but the overall website still needs improvement.
Domain Rating (DR) And URL Rating (UR) Are Important Signals Used By Search Engines To Determine The Credibility Of A Website And Its Pages, Directly Impacting Ranking Performance. By Acquiring High-Quality Backlinks, Optimizing Internal Link Structure, And Improving Content Quality, You Can Effectively Increase Both DR And UR, Thus Achieving Better Rankings And More Traffic In Search Engines. Understanding The Differences And Interactions Between The Two Can Help In Developing More Targeted SEO Optimization Strategies.
4、Technical Performance Ranking Signals
Technical Performance Ranking Signals Refer To The Technical Factors That Influence How Search Engines Evaluate And Rank Web Pages. These Signals Focus On The Website’s Security, Speed, And Stability, Ensuring That Users Have A Smooth And Secure Experience When Accessing The Page. Search Engines, Especially Google, Are Placing Increasing Importance On Technical Performance In Page Ranking Because These Factors Directly Affect User Experience And Satisfaction. Below Are Several Key Technical Performance Ranking Signals:
(1) Website security (HTTPS)
Website Security Is One Of The Fundamental And Important Ranking Signals. Using The HTTPS Protocol Encrypts Communication Between The User And The Website, Protecting Sensitive Information From Being Stolen. Google Has Clearly Stated That Websites That Enable HTTPS Will Receive Priority In Search Rankings Because Secure Sites Enhance User Trust And Reduce The Risk Of Information Leakage. Conversely, Websites That Do Not Enable HTTPS May Be Marked As “Not Secure” In Browsers, Which Can Affect User Click-Through Rates And Dwell Time, Thereby Indirectly Lowering Rankings.
(2) Website stability
Website Stability Refers To The Site’s Uptime And Reliability. Pages That Frequently Crash Or Fail To Load Are Considered Negative Signals By Search Engines, Affecting Indexing And Rankings. A Highly Stable Website Can Guarantee Over 99% Uptime, Providing Users With A Consistently Accessible Experience. Search Engines Tend To Rank Highly Stable Websites Higher Because These Sites Are More Likely To Meet User Needs.
(3) Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of performance metrics introduced by Google, primarily focusing on page load speed, interactivity, and visual stability. Optimizing Core Web Vitals can significantly enhance user experience, reduce bounce rates, increase time on site, and ultimately drive improvements in search rankings. Google has incorporated these metrics as an important part of its ranking algorithm, with well-optimized pages receiving higher ranking priority. The three key metrics included in Core Web Vitals are as follows:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time it takes for the main content of a page to load. The ideal time is under 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the time between a user’s first interaction with the page (such as clicking a button) and the browser’s response. The ideal value is under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures the unexpected visual shifts of page elements during the loading process. The ideal value is below 0.1.
The ranking improvement signals related to technical performance focus on the website's performance in terms of security, stability, and performance. Enabling HTTPS ensures data security, maintaining high website stability prevents downtime, and optimizing Core Web Vitals improves load speed and interactivity are key technical measures to improve a website's ranking in search engines. By continuously optimizing these technical aspects, websites can achieve higher visibility and user trust in search results, which in turn promotes traffic and conversion rate growth.
Ⅷ、SEO Link Building

SEO link building is a complex and long-term task that requires continuous patience and effort, based on a thorough understanding of its principles. The core of link building lies in enhancing a website’s authority and search engine ranking through high-quality external links. However, if there is a lack of clear understanding of the types and names of links, it’s easy to confuse different concepts in practice, which can affect the effectiveness of the strategy. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of various link types is crucial, including internal links, external links, backlinks, and their distinct roles in search engine optimization. In the case of external link (backlink) building, different types of links require different methods of acquisition. Moreover, the quality of links is more important than quantity. The evaluation criteria for backlinks include the relevance, authority, the use of anchor text, and other link forms. It is worth noting that link building is not without risks. Abusing link strategies, particularly using black-hat SEO tactics such as purchasing links or participating in link farms, can lead to penalties from search engines and even affect a website’s overall ranking. Therefore, during the link-building process, it is essential to follow search engine guidelines, focus on the naturalness and diversity of links, and avoid any practices that might trigger penalties. Through a systematic and compliant link-building strategy, long-term and stable results can be achieved in SEO optimization.
1、Types and Definitions of Links
(1) External links, backlinks, reverse links, and reference links
In SEO link building, terms like "external link," "outbound link," "backlink," "reverse link," and "citation link" are often used interchangeably. In fact, they all refer to the same type of link. These terms describe the action of third-party websites linking to a page on our site in various forms, such as anchor text, buttons, or direct URL placements. Despite the different names, their role and purpose in SEO are the same: to enhance our website's authority and search engine ranking through links from other websites. The reason for explaining these different terms is to help SEO beginners avoid confusion with terminology during their learning and practice process. Many newcomers might mistakenly think that these terms represent different types of links, leading to misunderstandings when formulating link-building strategies. Understanding the uniformity of these terms helps to clarify the core concept of backlinks, allowing focus on how to acquire high-quality third-party links, rather than getting bogged down in terminology differences. Whether referred to as external links or backlinks, their essence is to improve a website's visibility and authority in search engines. The key lies in the quality, relevance, and naturalness of the links, not the name itself.
(2) Referring domain
In SEO link building, "referring domains" is an important metric for evaluating the quality and diversity of external links to a website. It refers to the number of distinct external websites (domains) that link to our site. On the other hand, "external links" (backlinks) refer to the specific number of links pointing from other websites to ours. While the two are closely related, there is a distinct difference between them. For example, if 5 different websites each provide one link to our website, we have 5 referring domains and 5 backlinks. However, if one of those 5 websites provides 10 links, while the other 4 websites each provide 1 link, we still have 5 referring domains, but the total number of backlinks would be 14.
Referring domains emphasize the diversity of link sources. Search engines generally consider links from multiple independent domains to be more authoritative and trustworthy than a large number of links from the same website. This is because a variety of referring domains signals that our website is recognized in a broader network, helping to increase search engine trust in our site. While backlinks may be abundant, if they are primarily concentrated on just a few domains, search engines may view this as link manipulation or unnatural growth, which can harm SEO performance. Therefore, in a link building strategy, increasing the number of referring domains is more effective for improving a site's ranking and authority than simply increasing the number of backlinks.
(3) Internal links
In SEO link building, "internal links" and "internal linking" essentially refer to the same type of link, just under different names. These links refer to the connections between different pages within a website, such as linking from the homepage to a category page, or linking from one article to another related piece of content. The main purpose of internal links is to help both users and search engines better understand the website's structure, enhancing the relevance between pages and thereby optimizing the overall accessibility and ranking of the site. Internal links not only guide visitors to explore more content on the site, increasing page dwell time and browsing depth, but they also effectively pass page authority (link juice), giving important pages an advantage in search engine rankings. Additionally, a well-structured internal linking system helps search engine crawlers more efficiently crawl and index the website’s content. This is especially crucial for large websites, as optimizing internal links is key to ensuring that all important pages are properly indexed. Therefore, in SEO optimization, building internal links requires careful planning, using appropriate anchor texts and linking paths to enhance user experience and search engine friendliness.
(4) Outbound links and outbound anchor text
In SEO link building, "outbound links" and "outbound anchor texts" essentially refer to the same type of link, just under different names. These terms describe links from our own website pointing to external websites. Typically, outbound links are presented in the form of anchor texts, meaning that keywords or phrases are set as clickable links, directing users to relevant pages on other websites. Outbound links play an important role in SEO. Although they direct traffic away from our site to other websites, well-placed outbound links can actually enhance our site’s authority and credibility. Linking to high-quality, authoritative external sites signals to search engines that our content is reliable and valuable, helping to strengthen the thematic relevance and depth of our content. Additionally, outbound links can improve user experience by providing visitors with more useful information sources. However, the use of outbound links must be done with caution. Linking to low-quality or irrelevant websites can lead search engines to view the links as spammy, potentially harming the SEO performance of our own site. Therefore, in link building, it is crucial to carefully manage the use of outbound links and outbound anchor texts to optimize the overall performance of the website.
2、Functionality of All Link Types
(1) The Mechanism of Internal Links (Anchor Text Links) in SEO
In SEO, the role of internal links (anchor text links) primarily lies in the "voting mechanism" and the impact on rankings associated with anchor text keywords. Each internal link, especially those embedded in the form of anchor texts, effectively casts a "vote" for the target page's specific keyword. When search engine crawlers visit a website, they identify the keywords in these anchor texts and use them to determine the topic and relevance of the linked page. This "referral effect" can enhance the ranking of the linked page for the associated anchor text keyword. However, internal anchor text links generally have less impact on rankings compared to external links (backlinks), because external links are considered third-party "recommendations" with higher authority and credibility. Despite this, internal links still play a crucial role in SEO optimization. By strategically positioning anchor text links, you can effectively guide search engine crawling paths and ensure that important pages receive more exposure and link equity. Additionally, internal links can improve user experience by helping visitors navigate to related content, increasing time spent on the site and interaction depth. While internal anchor links have a weaker ranking influence, their role in site structure optimization and keyword distribution should not be overlooked.
(2) The Mechanism of External Links (Backlink Anchor Text Links) in SEO
In SEO, the role of external links (backlink anchor text links) is widely regarded as one of the core factors in boosting website authority and keyword rankings. Each external backlink, particularly one that uses anchor text, can be viewed as a "vote" or "recommendation" for the target page's specific keyword. Search engines treat these external links as crucial signals of a page's authority and credibility, especially when they come from high-authority and highly relevant websites. Keywords in backlink anchor texts directly impact the search ranking of the linked page. For instance, if multiple high-quality websites link to a page using the same or related anchor text, search engines will recognize the page as having high authority and relevance in the subject area, thereby improving its ranking. This "referral effect" of external links is far more impactful than internal links because it represents third-party validation of the content, which search engines generally consider more trustworthy than self-promotion. Moreover, the quality and diversity of backlinks are key metrics that search engines use for evaluation. Backlinks from different referring domains increase the website's trustworthiness, preventing the links from being seen as manipulative. Therefore, building high-quality backlink anchor text links not only improves keyword rankings but also strengthens the overall SEO performance and consolidates the website's authority in search engines.
(3) The Mechanism of Outbound Links (Anchor Text Links) in SEO
In SEO, the role of outbound links (anchor text links) mainly lies in enhancing the authority and relevance of the website's content, as well as improving user experience. Outbound links refer to links from our website to other external websites, usually presented in the form of anchor text, where specific keywords or phrases are made clickable, directing users to relevant external content. Although outbound links might redirect traffic from our website to other sites, they still play a positive role in SEO optimization. First, outbound links signal to search engines that the content of our website is built on authoritative and reliable information. When we link to high-quality and highly relevant external resources, search engines interpret it as a sign that we are providing valuable information, which boosts the credibility and authority of our website. This practice helps enhance the depth and breadth of the page's content and improves the site's professional image in specific areas.
Secondly, outbound links help search engines better understand the topic and context of our webpage. When the anchor text in the link is closely related to the content on the page, search engines treat these links as relevant supplements to the page’s theme, thereby improving the page’s ranking for related keywords. While outbound links do not directly influence ranking like backlinks do, they help establish the website's position in the information network, creating a healthy link ecosystem. Finally, outbound links significantly enhance user experience by providing visitors with more high-quality information sources, meeting their broader needs, and increasing trust and user retention. Therefore, wisely using outbound links not only optimizes SEO performance but also improves overall content quality and user satisfaction.
3. Types of External Links
(1) Natural External Links (Backlinks)
Natural external links (backlinks) are those that other websites create without any human intervention or exchange. These links typically arise because our website's content is of high value, quality, or authority, attracting voluntary references or recommendations from third-party websites. Whether in the form of anchor text or direct URL placement, these links emerge because of the intrinsic appeal of the content itself. Natural external links are considered the healthiest and most organic type of link in SEO, as they are entirely based on the genuine value of the content rather than being purchased, exchanged, or manipulated. Search engines trust these types of links more because they are seen as authentic user behavior and strong evidence of the website's authority, helping to improve the site's ranking and overall reputation.
(2) Internal Network Transmission of External Links (Backlinks)
Internal network transmission of external links (backlinks) refers to the practice of using multiple related websites owned by the same entity to create links that boost the weight and ranking of a target site. This type of linking often appears within link networks where multiple websites interlink to enhance SEO results. However, this practice requires caution because it may not fully comply with search engine guidelines. Search engines tend to encourage natural, authentic external links, while link network transmission can sometimes be seen as an attempt to manipulate rankings, potentially resulting in penalties. Despite this, if the sites within the network are highly relevant in terms of content and themes, and the links appear more natural and user-friendly, they might approach the search engine guidelines. For example, resource sharing and content recommendations among professional websites in the same field could be seen as legitimate link-building behavior. However, if the websites are unrelated or the links are too frequent or patterned, search engines may take notice and penalize the site. Thus, when using internal network transmission for external links, it is critical to consider its risks and ensure the naturality and relevance of the links.
(3) Business Negotiation Link Cooperation
Business negotiation link cooperation is an external link-building method that is reached through mutual negotiation, often involving a formal cooperation agreement or conditions. This type of link cooperation can manifest as traditional reciprocal link exchanges, where two websites mutually place each other's links to boost traffic and link equity. However, business negotiation link cooperation goes beyond simple link exchanges and may involve a variety of value exchanges, such as content collaboration, brand exposure, ad space swaps, or even mutual product or service offers as prerequisites for linking. This method is common in SEO, especially between websites that are somewhat well-known within their industry. Resource sharing can result in a win-win scenario. Nevertheless, business negotiation link cooperation must still be approached with caution to ensure its naturalness and relevance. Over-commercializing or creating unnatural links can lead search engines to view them as manipulative, which could harm SEO performance.
4. Methods for Building External Links
(1) Methods for Building Natural External Links (Backlinks)
By employing a combination of the following methods, it is possible to effectively build natural external links and increase a website's authority and search engine ranking. These methods include: The next part would continue with a list of methods for building backlinks.
Manually create backlinks
Posting high-quality content or valuable comments with links pointing to your own website on Q&A platforms, forums, and social media can be a simple method for gaining external links. However, the quality of the external links obtained through this method is typically low, so they should not make up a large proportion of the overall link structure to avoid being flagged as low-quality links by search engines, which could affect the website's authority.
Enhance Content Quality
Create content with high value, deep insights, or unique perspectives to increase the likelihood of being referenced by other websites. High-quality content is more likely to earn natural external links, especially citations from authoritative industry websites or blogs.
Guest Posts for Building External Links
Write guest posts for relevant industry websites or blogs and naturally embed links to your own site within the content. This not only provides external links but also boosts brand exposure and authority.
Replace your competitor’s 404 links
By using the 404 link checker tool, you can find broken links (404 pages) on competitor websites and contact the source websites to suggest replacing those links with links to your own website. This method not only helps the other party fix their broken links but also earns you a high-quality external link.
Contact Industry Resource Websites
Proactively seek and reach out to industry resource websites, such as directory sites, industry association websites, etc., to discuss external link building. These sites typically have higher authority, and the link quality is generally good.
Collaborate with Industry Bloggers or Video Creators
Contact bloggers or video creators within your industry and offer product reviews or content collaborations in exchange for external links on their pages. This method effectively increases brand exposure while securing high-quality external links.
Link Bait Strategy
Attract external links through specific types of content. Common types of link bait include: The list of link bait strategies would follow in the original content.
- Data Source Bait: Publish in-depth data analysis, survey reports, or original research to attract citations from other websites.
- Controversial Bait: Create content that presents controversial or challenges traditional viewpoints, sparking discussions and citations.
- Online Tools or Plugin Bait: Develop practical or interesting free tools or plugins that attract users and websites to share links.
- Humorous Content Bait: Create humorous and engaging content to increase the likelihood of social media shares and website citations.
(2) How to build your own site group to transmit external links (backward links)
Building your own link network (PBN) for transmitting external links (backlinks) is a more complex and technically demanding SEO strategy. This method involves creating multiple websites (a "PBN") to exchange external links with each other, thereby improving the main site's authority and search engine ranking. However, implementing this strategy requires deep knowledge of computer science and a significant investment of resources. First, building a PBN is not simply about setting up multiple websites. Each website needs its own independent server or IP address to avoid being recognized as a form of cheating by search engines. Additionally, to ensure the effectiveness of the PBN, these websites must maintain differentiation in terms of content, structure, and themes to prevent search engines from penalizing for duplicate content. This requires developers to have diversified content production capabilities and solid website architecture design skills, as well as a deep understanding of search engine algorithms to avoid potential risks.
Maintaining an effective network of websites (also known as a "website farm") requires continuous human and time investment. Each site needs to be regularly updated with content, undergo security maintenance, and implement routine SEO functions to ensure its proper operation and maintain a certain level of traffic. This not only requires SEO optimization skills but also expertise in server management, network security, and data analysis. The workload within these specialized IT areas would require a small or medium-sized technical team to handle effectively. Moreover, the operational costs of a website farm are quite high, including domain registration, server rentals, content creation, and technical support, all of which add up to a significant expense. Due to the complexity and high cost of building a website farm, this method of external link building is not suitable for most businesses and website owners. For small to medium-sized businesses or individual webmasters, a more feasible approach is to enhance website authority through high-quality content creation, natural link acquisition, and social media promotion, rather than relying on a website farm strategy that demands strong technical skills and incurs high costs. Although using a website farm for external link transmission may provide short-term ranking improvements, once search engines identify it as a violation, it can lead to severe penalties or even complete removal from search engine indexes. Therefore, unless you possess sufficient technical capabilities and resources, and can bear the associated risks, this method is not recommended.
(3) Methods for Building Business Link Cooperation
Business link cooperation is one of the more common and effective methods in SEO external link strategies. By establishing direct partnerships with other websites or bloggers, you can obtain high-quality external links, which helps improve your website's authority and visibility in search engines. Below are common execution methods for building business link cooperation:
Target Website Selection and Analysis
Before initiating any collaboration, you first need to define the criteria for selecting target websites. Ideal cooperation partners should have the following characteristics: related or complementary to your website's theme, a high domain authority and credibility, stable traffic, and an active user base. Additionally, you can use SEO tools (such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz) to analyze the backlink profile, traffic sources, and audience demographics of the target website, ensuring that these links provide real SEO value for your website.
Personalized Communication and Value Demonstration
When reaching out to target websites or bloggers, avoid using generic emails. Instead, tailor your communication based on the content and style of the recipient's website, demonstrating an understanding and appreciation of their work. Clearly outline the potential collaboration methods, such as link exchanges, guest posts, co-marketing content, or hosting joint online events. Highlight the win-win value of the collaboration, such as bringing new traffic, brand exposure, or providing high-quality original content to the partner.
Provide High-Quality Content or Resources
The core of business link cooperation is offering attractive exchange conditions. In addition to standard link exchanges, you can create valuable content for the partner website, such as writing high-quality guest posts, producing infographics, or providing industry reports. You can also offer exclusive tools, data analysis, or professional advice, further increasing the likelihood of cooperation.
Long-Term Relationship Maintenance and Cooperation Expansion
Business link cooperation should not be a one-time transaction but should aim to build long-term relationships. After reaching an agreement, regularly communicate with the partner to share new content or resources and explore further collaboration opportunities. By deepening the cooperation over time, you can gradually build a stable network of external links.
Tracking and Optimizing Cooperation Outcomes
After the collaboration is established, it is important to continuously monitor the effect of external links and evaluate their impact on website traffic and SEO rankings. Tools such as Google Analytics and Search Console can be used to track the traffic and user behavior generated by the links, analyzing which types of collaborations are the most effective, and optimizing future link-building strategies.
Avoiding Potential Risks and Ensuring Link Naturalness
When negotiating collaborations, it’s crucial to ensure the naturalness and diversity of the links, avoiding excessive anchor text optimization that could be viewed by search engines as link manipulation. Additionally, the partner website should be high-quality and compliant, avoiding links from low-quality or non-compliant sites that could negatively affect the SEO performance of your own website.
5. External Link (Backlink) Evaluation Metrics
External link (backlink) evaluation metrics are essential tools for assessing the quality and effectiveness of links, directly impacting the success of SEO optimization. By systematically evaluating the following metrics, you can better filter high-quality backlink resources and ensure the effectiveness and safety of your SEO link-building efforts. Below are specific evaluation metrics and their corresponding content:
(1) Page Content Relevance
The relevance of the content on the page containing the external link to your website’s theme and keywords. The higher the relevance, the more trusted the link will be by search engines, which helps improve your website's authority. Irrelevant external links may be considered spam links, significantly reducing their effectiveness.
(2) Domain Rating (DR) and Page Authority (UR)
DR measures the authority of the entire domain, while UR measures the authority of a specific page. High-quality external links should come from websites and pages with high DR and UR. Tools like Ahrefs can quickly provide these metrics, and links from high DR and UR pages are more beneficial for improving your site’s SEO performance.
(3) Domain Age (Older domains are more trusted)
The longer a domain has existed, the more trusted it generally is by search engines. Older domains indicate a certain level of historical accumulation and stability, making backlinks from such sites more authoritative.
(4) Domain Ownership History (Has the domain changed hands or categories?)
If the domain has been transferred or the website's category has changed, it may affect the trustworthiness of the domain. You can check the historical records through WHOIS to ensure that the linking source website maintains consistency in content and purpose.
(5) Number of Outbound Links on the Website
If a target website has too many outbound links, the weight of each external link will be diluted, affecting SEO performance. Ideal link sources are websites with fewer outbound links and a focus on high-quality content. Conversely, if the source website has a low DR or excessive outbound links, the value of the external link will be significantly reduced.
(6) Placement of Anchor Text Links
The location of the link directly affects its value. High-quality external links should be placed within the main content area of the page, such as within the body text, rather than in the footer or sidebar.
- Anchor Text Placement for Communication (Adding External Links on Other Pages): It is important to request that the link be placed in the main content of the homepage or article page in the form of anchor text, avoiding placement in the footer or sidebar.
- External Links When Providing Articles: If acquiring links through guest posts, the anchor text can be naturally embedded directly within the article content while writing.
(7) Agreement on the Article Retention Period
The longevity of backlinks is crucial for SEO. In collaborations, it’s important to establish that the article and anchor text will be retained long-term and not be deleted arbitrarily. Normally, published articles should be kept permanently to ensure the external link remains effective over time.
(8) Ensure Dofollow Links or Acquire Traffic
Ensure that the link is dofollow, so that search engines can track and pass on authority. Also, make sure that the linked page does not use the noindex tag, otherwise search engines will ignore the page, which will affect the effectiveness of the backlink. If the other party cannot provide a dofollow link, but the page has excellent traffic evaluation, and if it's confirmed that the external link can generate some commercial value from the traffic on the page, it is still beneficial and acceptable for us.
(9) Analyze the Traffic of the Link Source Page
Evaluate the traffic of the page where the link originates. High-traffic pages not only help pass on authority but also drive direct traffic to your website. Tools like Google Analytics can help retrieve this data.
(10) Evaluate Website and Page Health, and Check for Past Search Engine Penalties
Moz Spam Score Metric
Check the target website's Spam Score, a high score may indicate that the website has spammy link practices or other violations.
Traffic Trend Analysis
By analyzing traffic trends, you can assess if the website has ever been penalized. A sharp decline in traffic could indicate that the website has been penalized by search engines.
Search for Brand Names and Keywords
If the website's name or primary keywords don't appear on the search results' first page or are missing from the index altogether, it could indicate the site has been penalized. Be cautious when collaborating with such sites.
(11) Anchor Text Should Be Natural
Using keywords as anchor text is effective, but excessive optimization can result in search engine penalties. Anchor text should be diversified, avoiding the overuse of exact-match keywords. The best approach is to naturally incorporate keywords into fluent, contextual language.
(12) Evaluate the Cost and Return of Link Acquisition
Evaluate the cost and return of acquiring backlinks. Some links may require high payments or substantial resources. If the cost is too high and the return is limited, carefully consider whether it is worth the investment.
(13) Quality of the Target Website’s Own Backlinks
Check the quality of backlinks on the target website. If the site’s backlinks are predominantly low-quality or spammy, it suggests that the website’s SEO practices are questionable, which could negatively impact the quality of your backlinks.
(14) Ranking Ability of Keywords on the Target Website
Analyze how well the target website ranks for its primary keywords. Pages that rank well indicate effective SEO optimization, and obtaining backlinks from such pages can significantly improve your own keyword rankings.
6. Link Building Precautions to Avoid Search Engine Penalties
To ensure safe and stable SEO optimization, it’s important to avoid practices that could lead to penalties. Following these guidelines can help reduce the risk of penalties during the link-building process, ensuring your website's long-term, stable growth. The following precautions can effectively minimize the risk of penalties during backlink construction:
(1) Maintain Steady Growth of External Links, Avoid Sudden Spikes
Link growth should follow a natural pace, avoiding a sudden increase in backlinks over a short period. Abrupt spikes in the number of backlinks can be perceived as unnatural behavior by search engines, potentially leading to penalties or de-ranking.
(2) Avoid Link Farms
Link farms are websites dedicated to selling large quantities of low-quality backlinks. Participating in link exchanges on such platforms will be viewed as black-hat SEO by search engines, which can result in penalties or removal from search indexes.
(3) Avoid Large-Scale Link Exchanges
Mass link exchanges (e.g., Site A links to Site B, and Site B links back to Site A) are recognized by search engines as ranking manipulation and can dilute the value of the backlinks, potentially leading to penalties. Moderate and natural link exchanges are the safest approach.
(4) External Links in Plugin Source Code Should Be Compliant
If external links are embedded in plugin source code, make sure that the link placement is reasonable and complies with guidelines. Hidden or irrelevant links may be identified as spam by search engines, risking penalties for both the plugin and your website.
(5) Avoid Using Link Bait Tools or Plugins in Gray Markets
Ensure that plugins or tools are not abused by gray markets (e.g., gambling, adult content, etc.). If a plugin is widely used on illegal websites, it may indirectly harm your website’s reputation and backlink quality, increasing the risk of search engine penalties.
(6) Marketing Links Should Include Nofollow or Sponsored Tags
All paid advertising and marketing-related links should include the nofollow or sponsored attribute to inform search engines that these links do not participate in ranking calculations. Paid links without the attribute may be considered as manipulating rankings, leading to penalties.
(7) Avoid Submitting Links to Low-Quality Website Directories
Avoid submitting backlinks to low-quality or spam directories. Such directories are usually considered irrelevant or worthless by search engines, which may harm your SEO performance. Opt for authoritative and highly relevant directories to submit your links for greater safety.
(8) Maintain Diversity in Link Sources and Anchor Text
Ensure diversity in the sources of external links, avoiding over-concentration on just a few websites. Also, diversify the anchor text to prevent overuse of the same keywords. Single-source links and repetitive anchor texts are often seen as unnatural by search engines, increasing the risk of penalties.
(9) Choose Websites with Infrequent Advertising for External Link Cooperation
When selecting websites for external link cooperation, avoid sites that frequently sell advertising or backlinks. Such sites are often regarded as low-quality by search engines, and backlinks from them may have little value or even have a negative impact.
(10) Websites Should Not Be Used as Platforms for Spam Links
Ensure that the comment sections or forums of your website have a moderation mechanism to prevent spam links (e.g., gambling or adult content). Uncontrolled spam links can reduce your website’s trustworthiness and even result in search engine penalties.
(11) Avoid Keyword Stuffing in Content Creation
In content creation, avoid the practice of excessive keyword repetition (keyword stuffing). This approach is recognized as over-optimization by search engines and can harm your page’s rankings, potentially even resulting in penalties.
(12) Do Not Create Content Irrelevant to the Website’s Niche
Link-building should be focused on content related to your website’s theme. Publishing a large number of irrelevant links not only fails to improve authority but may also be seen as spam by search engines, negatively impacting the overall ranking of the site.
7、Summary of External Link (Backlink) Building
There are various methods for SEO link building, but that doesn’t mean all methods must be implemented. It’s neither realistic nor necessary. After trying different link building strategies, it’s most effective to find the approach that best suits the website’s characteristics and resource advantages, and continuously accumulate experience based on that. In fact, many simple methods, when done to perfection, often produce the most significant results. Therefore, instead of pursuing complex backlink strategies, it’s better to focus on areas of expertise and continue to optimize and improve. However, in the overall SEO strategy, external link building is not the most important part. The quality and quantity of content are the core of SEO, and external link building must be built on the foundation of high-quality content. Without high-quality content, no amount of external links will produce the expected results. Google search engine especially values the ranking weight of high-quality content, and the role of quality content far exceeds that of external links. Google’s algorithm tends to assign higher rankings to pages that provide valuable information, rather than simply relying on the number of links to determine a page's authority.
In addition, through understanding the "principles of action for all types of links," it becomes clear that keyword rankings cannot only rely on external links for improvement. We can fully control internal links and outbound links, which also play an important role in SEO. A well-structured internal link setup helps to improve the overall authority and user experience of the website, while high-quality outbound links can enhance the page's authority and boost the credibility of the content. Therefore, possessing high-quality content creation skills and being proficient at constructing reasonable internal and outbound links can also achieve excellent Google SEO results.
For startups, external link building often requires a significant amount of human and material resources, and the process can be cumbersome and complex, which may not be suitable for resource-limited teams. Many people mistakenly believe that link building is a shortcut to improving rankings, but in reality, all manually created links may be considered non-compliant, though to varying degrees. The closer the link building is to being compliant, the harder it is to implement. Limiting the focus to link building will restrict the development space for SEO strategies and may even backfire. Therefore, the blogger suggests that startups should invest more effort into creating high-quality content when building external links. By consistently producing valuable content, attracting natural backlinks and user shares, the website's authority and ranking will improve in a healthier, more stable way. High-quality content is the strongest foundation for SEO, and this is the shortest path to achieving SEO results. Instead of spending substantial resources on building external links with uncertain results, it is better to focus on improving content quality and allowing external links to grow naturally, achieving sustainable SEO optimization.
Ⅸ、Reasons for SEO Traffic (Ranking) Drops and Solutions
SEO traffic and ranking declines are common issues faced by many websites during their operation, and they can be caused by a variety of factors, both external and related to the website’s optimization strategy. Search engine penalties and algorithm updates are often the primary reasons for traffic fluctuations, especially if the site violates rules or fails to update its optimization strategy in time. Additionally, technical issues on the website, the loss of high-quality backlinks, and negative SEO attacks can directly impact rankings. Apart from technical factors and external links, content timeliness and market competition are also crucial. Over time, outdated content and a decline in topic popularity can lead to traffic loss, while emerging, higher-quality competing content may replace the original page’s ranking. Therefore, maintaining website technical stability, continuously optimizing content, and adapting to the latest changes in search engine algorithms are effective ways to cope with SEO traffic decline. Below are the reasons for SEO traffic declines (ranking drops) and corresponding solutions:
1、Common Reasons for Search Engine Penalties
When a website violates search engine guidelines or uses unethical SEO techniques, it may face penalties from search engines. The consequences of being penalized typically manifest as a drop in rankings or removal from search engine results. Once penalized, active corrective measures need to be taken, such as removing harmful links, updating or deleting duplicate content, and improving user experience, to restore the website’s rankings and traffic. Here are some common reasons that could lead to a website being penalized by search engines:
(1)Over-optimization
Using excessive keyword stuffing, overly optimized titles and meta descriptions, or manipulating rankings through hidden text and links can be detected by search engines, resulting in a penalty.
(2)Buying Links
Purchasing unnatural backlinks to boost a website’s ranking is seen as “ranking manipulation” by search engines (such as Google), which could lead to a penalty or even complete removal from the index.
(3)Poor Link Building
If a website has many spammy links (such as low-quality directories or reciprocal links), search engines may deem the website as untrustworthy, leading to a penalty.
(4)Duplicate or Plagiarized Content
Copying or plagiarizing content violates search engine content policies, which can lead to a drop in rankings or even complete removal from the index.
(5)Using Black Hat SEO Techniques
Techniques such as hidden text, hidden links, and excessive anchor text optimization are considered black hat SEO. Search engines penalize websites when these tactics are detected.
(6)Non-compliance with Google’s Quality Guidelines
If the website content does not comply with Google's Quality Guidelines, such as low-quality content, untrustworthy ads, or confusing page layouts, the website may face penalties.
2、Ranking Fluctuations Caused by Search Engine Algorithm Updates
Search engines (such as Google) regularly update their algorithms to provide higher quality and more relevant search results. These algorithm updates can directly affect a website’s rankings, leading to traffic fluctuations, especially if the website’s content or structure does not adapt to the new rules. Here are common scenarios where algorithm updates can cause ranking fluctuations:
(1)Core Algorithm Updates
Google conducts several core algorithm updates each year, aimed at improving the overall quality of search results. These updates typically do not target specific websites, but if a website’s content quality is low or the user experience is poor, rankings may be affected.
Algorithm Updates Targeting Specific Issues
- Panda Algorithm: Primarily targets low-quality, duplicate content, and content farms, aiming to improve the ranking of original, high-quality content.
- Penguin Algorithm: Focuses on unnatural link building and over-optimization, penalizing spammy links and black-hat SEO tactics.
- Hummingbird Algorithm: Improves understanding of natural language searches, impacting the accuracy of keyword matching.
- Pigeon Algorithm: Enhances the accuracy of local search results, optimizing local SEO performance.
(3) BERT and AI-driven updates
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and other AI algorithm updates have improved search engines' ability to understand semantics and context. If the content structure is unclear or lacks semantic relevance, it may be impacted.
(4) How to deal with ranking fluctuations caused by algorithm updates
- Maintain High-Quality Content: Regularly update original and in-depth content, avoiding low-quality and duplicate information.
- Optimize User Experience: Improve page load speed, enhance mobile experience, and ensure a clear website structure.
- Natural Link Building: Focus on acquiring high-quality, natural backlinks and avoid purchasing or exchanging links.
- Monitor Traffic and Rankings: Use tools (such as Google Search Console) to track ranking changes and adjust optimization strategies in a timely manner.
- To stay updated on the latest algorithm changes: Follow the Google Official Announcements or SEO communities to stay informed about algorithm updates and adjust strategies accordingly.
3、Technical Failures Leading to Page Rank Decline
Technical failures on a website are one of the common reasons for SEO traffic drops. Even if content and backlink strategies are in good shape, technical issues can severely impact how search engines crawl, index, and rank a website. Below are some common technical issues, their potential impact on SEO, and methods for troubleshooting and fixing these issues. Regularly checking and optimizing technical details can effectively prevent SEO traffic decline caused by technical failures.
(1) Incorrect HTTPS Configuration or Lack of HTTPS
Search engines like Google consider HTTPS as a ranking factor. If a website does not enable HTTPS or if the SSL certificate is improperly configured (e.g., expired certificate or mixed content warnings), search engines may lower their trust in the website, which can negatively impact rankings.
(2) Slow Page Load Speed
Page load speed is an important factor for both user experience and SEO rankings. The following issues can slow down load speed:
- Uncompressed or oversized images
- Excessive use of JavaScript or CSS files that are not optimized.
- Cache not enabled or misconfigured
- Using low-performance Hosting or CDN with incorrect configuration.
- Slow page load speed not only increases bounce rates but also directly impacts rankings on search engine results pages.
(3) Server Downtime or Frequent Failures
If a server experiences frequent downtimes or has long response times, search engine crawlers may encounter errors (such as 5xx server errors) when accessing the site. Pages that are unavailable for a long period may be removed from the index, resulting in a significant ranking drop.
(4) Incorrect Sitemap Settings
A sitemap helps search engines crawl and index pages more efficiently. If the sitemap is incorrectly configured, it may lead to:
- Including deleted or invalid URLs
- Not including important pages, causing them not to be indexed
- Not submitting the sitemap correctly to Google Search Console or having formatting errors
These errors can hinder comprehensive crawling by search engines, resulting in pages not being indexed or rankings declining.
(5) Incorrect robots.txt Settings
The robots.txt file guides search engine crawlers on how to crawl the site. If incorrectly configured, it may:
- Block important pages or the entire site from being crawled
- Fail to allow crawlers to index important directories, causing key content not to be indexed
- Check whether the robots.txt file has mistakenly used the
DisallowDirective, especially for important directories or files.
(6) Incorrect Handling of URL Structure Changes
Changing a website’s URL structure without setting up 301 redirects can cause old URLs to become invalid, affecting how search engines index and rank pages. Additionally, using too many dynamic URL parameters or overly complex URLs can also negatively impact SEO performance.
(7) Duplicate Content or Incorrect Use of Canonical Tags
Technical duplicate content (e.g., the same content displayed on different URLs) can make it difficult for search engines to determine which page should rank. If canonical tags are set incorrectly, they may point to the wrong page, causing weight distribution issues or preventing important pages from being indexed.
(8) Mobile Optimization Issues
Search engines prioritize indexing the mobile version of a website. If there are mobile compatibility issues, such as broken layouts, difficult-to-click buttons, or unreadably small fonts, mobile rankings may drop, impacting overall traffic.
(9) Incorrect Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Incorrectly implemented structured data markup can cause search engines to misinterpret the page’s content, leading to issues with rich snippets (such as star ratings or product info), which may lower click-through rates and rankings.
(10) Website Security Issues (e.g., Hacked Sites)
If a website is infected with malicious code, spam links, or flagged as insecure by search engines, it can cause a significant drop in traffic. Additionally, security warnings displayed to users can significantly increase bounce rates.
(11) How to troubleshoot and fix technical problems
- Use Tools To Detect Issues: For example, use Google Search Console to check for crawl errors and index status, PageSpeed Insights to test loading speed, and SSL Labs to check HTTPS configuration.
- Regularly Check robots.txt and Sitemap: Ensure proper configuration and submit the latest versions to search engines.
- Set Up Monitoring and Backups: Use server monitoring tools to detect downtime, and regularly back up website data to ensure quick recovery.
- Optimize Mobile Experience And Loading Speed: Ensure the website has a well-implemented responsive design, enable caching and CDN, and compress images and code.
- Keep Security Updates Current: Regularly update the CMS, plugins, and server security patches, and use firewalls and security plugins to prevent hacking attempts.
4、Loss of High-Quality Backlinks Leading to Page Rank Decline
Backlinks are a critical ranking factor in SEO, particularly high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites, which can significantly enhance a site's trustworthiness and authority. However, when these high-quality backlinks are lost, it can directly lead to a decline in page rank and traffic. Below are some common reasons and impacts of losing high-quality backlinks, along with methods to monitor and maintain backlink quality to effectively reduce the negative impact on rankings and maintain SEO competitiveness.
(1) Backlink Page Deleted or Redirected
If the pages linking to your website are deleted or incorrectly Redirected (such as not setting up a 301 redirect), the external links originally pointing to your site will become invalid. This can result in a loss of link equity for your website, which in turn may negatively impact its rankings.
(2) Content of the Backlink Modified or Removed
The content linking to your website may be modified or removed due to site updates or content changes, causing the backlink to become ineffective or converted into a nofollow link, which will no longer pass on authority.
(3) Decline in the Linking Site’s Authority or Penalty
If the authoritative website linking to your site is penalized by search engines due to violations or poor content quality, the authority of these backlinks will also be diminished, which can affect your site's ranking.
(4) Backlink Changes to Nofollow Attribute
A nofollow attribute on a backlink prevents search engines from passing authority through the link. If a previously dofollow backlink is changed to nofollow, it may lead to a decrease in page authority.
(5) Partner or Media Website Goes Offline
Some backlinks may come from partner websites or news media sites. If these sites shut down or go offline, you will lose these high-quality backlinks, resulting in a decline in ranking.
(6) Competitor’s Backlink Strategy
Competitors may surpass your website by building more or better backlinks. If your site loses key backlinks while competitors continue to improve their backlink profiles, your ranking may be negatively impacted.
(7) Website Migration or URL Structure Change Without Updating Backlinks
If your website undergoes migration or changes its URL structure without notifying backlink sources or updating the backlink addresses, the original backlinks may point to invalid pages (404 errors), leading to a loss of authority.
(8) Link Exploitation (Negative SEO)
In some extreme cases, malicious competitors may attempt to negatively affect your ranking by deleting or requesting the removal of high-quality backlinks to your site.
(9) The impact of losing high-quality external links
- Page Weight Decrease: External links are an important way to pass page authority, and the loss of high-quality external links directly reduces the page's weight.
- Decreased Trust: A reduction in authoritative external links may be interpreted by search engines as a decline in the website's popularity, which affects overall trustworthiness.
- Keyword Ranking Drop: The loss of external links weakens a specific page's competitiveness for relevant keywords, leading to a drop in rankings.
- Traffic Reduction: Losing high-quality external links also reduces direct referral traffic from those links, affecting overall website visits.
(10) How to detect and respond to the loss of high-quality external links
Monitor External Links with Tools
Use SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Google Search Console to regularly monitor external link status and identify lost high-quality links.
Restore Lost External Links
- Contact the website administrator of the external link source to inquire about the reason for the link removal and request its restoration.
- If the external link page has been deleted, try offering updated content or link to a new page.
- Ensure that partners and media are aware of your website's latest URL structure to avoid broken links due to URL changes.
Continually Build High-Quality External Links
- Create valuable content that naturally attracts external links.
- Participate in industry discussions, publish high-quality guest articles, and expand new external link sources.
- Maintain long-term partnerships with authoritative websites and media to ensure the stability of external links.
Check Internal Links and Redirects
Set up correct 301 redirects within the website to ensure that even if external links point to old pages, the link equity will be passed to the new pages.
Competitor Analysis
Regularly analyze competitors' external link strategies to find new external link opportunities and recover lost link equity.
Ⅹ、Ways to Improve SEO Click-Through Rate (Increase Traffic)
的方法.png)
In the process of improving SEO click-through rates (and subsequently driving traffic growth), multiple key strategies need to be systematically applied and optimized. First and foremost, optimizing keywords in titles and descriptions is crucial. By naturally integrating commonly searched terms into the title and meta description, you can significantly enhance the page's appeal in search results. Additionally, using attractive title and description formats, such as incorporating numbers, question phrases, or emotional language, can further spark users' desire to click. To enhance the visual appeal of search results, optimizing with rich media content (such as videos and images) is also essential. This not only diversifies the way search results are displayed but also boosts user interest in the page. Moreover, adding the latest date or update time to the title or description can create a sense of content timeliness, increasing the likelihood of clicks.
On the technical side, using clearer and more descriptive URLs not only facilitates search engine crawling but also helps users understand the page content, which in turn boosts click-through rates. Adding structured data is another important optimization measure; it helps search engines better understand page content and display it in rich snippets in search results, increasing the page's visibility and click-through rate. Page load speed is also a key factor influencing click-through rates. Fast-loading pages provide a better user experience and reduce bounce rates caused by long wait times. Additionally, optimizing for local searches, such as adding Google My Business information, can effectively enhance visibility in local searches, attracting more clicks from local users.
1、Optimize Keywords in Titles and Descriptions
(1) Put the core keywords at the beginning of the title
Search engines and users tend to focus more on the first few words of a title. Placing the most important keywords at the beginning of the title helps improve the page's search ranking and increases the likelihood of user clicks. For example, "Independent Site Building Guide: Create A Cross-Border E-Commerce Website From Scratch" places "Independent Site Building" at the beginning to highlight the core content.
(2)Keep the title concise and attractive
Although keywords are important, stuffing keywords will make the title lengthy and unreadable. Keep the title length within 29 characters to ensure that it is fully displayed in search results, while keeping the language fluent and natural to enhance appeal.
2、Use Attractive Title and Description Formats
(1) Use numbers and special symbols to increase appeal
Adding numbers (such as "5 ways", "2025 latest guide") or special symbols (such as "|", "-") in the title can increase the click-through rate. Numbers make users feel that the content is specific and easy to understand, while symbols can make the title more hierarchical and easy to recognize.
(2) Ask questions and stimulate curiosity
Using a question format in the title can spark users' curiosity. For example, "Why Does Your Coffee Machine Always Fail To Brew Rich Coffee?" or "Do You Really Know Which Wireless Earbuds Suit You Best?"—these types of titles guide users to click and seek answers.
(3) Use powerful verbs and emotional words
Verbs and emotional words can enhance the attractiveness of the title, making the content appear more action-oriented and emotionally resonant. For example, "Unlock These Tips to Easily Choose the Perfect Air Fryer" or "Avoid These Pitfalls to Find Truly Effective Skincare Products", this type of expression makes users feel that the content is practical and urgent.
(4) Create a sense of urgency and scarcity
Adding time-limited or scarcity-related words in the title or description can stimulate users' desire to click. For example, "Limited-Time Offer: The Most Popular Smart Home Products of 2025" or "Only This Week! Don't Miss These High-Performance Smartphone Recommendations", making users feel that they will miss important information if they don't click.
(5)Directly related to user needs
Ensure that the title and description directly address users' pain points, highlighting the practical value of the content. For example, "How to Choose the Right Skincare Products? Avoid These 3 Common Mistakes" or "Must-See 2025 High-Cost Performance Laptop Recommendations", clearly stating the benefits the content can bring to the users, which helps improve the click-through rate.
(6) Use words that convey authority and credibility
Adding authoritative or trustworthy words in the title can increase users' trust in the content. For example, "Expert Recommended High-Performance Robotic Vacuums" or "Top Smartphones of 2025: User Reviews Unveiled" will make users feel that the content is authoritative and more likely to click to learn more.
(7) Personalized content to fit the target group
Adjust the title style according to the target audience's interests and needs to make it more personalized. For example, for younger users, use trendy language, such as "These 5 Headphones Will Make You Instantly Cool", while for family users, emphasize practicality, such as "Essential for Families: Energy-efficient and Practical Air Conditioner Recommendations". This personalized strategy can effectively increase the click-through rate of the target group.
3、Use Rich Media (Videos, Images) to Enhance Search Result Displays
(1) Embed high-quality images and videos in your content
High-quality images and videos can enhance the visual appeal of a webpage and improve user experience. Search engines are more likely to recommend pages rich in multimedia content, especially in Google Image Search and Video Search. Make sure to use high-definition, clear images and upload optimized versions with suitable resolution for webpage loading, avoiding any impact on page load speed.
(2) Add descriptive ALT text and titles to images and videos
ALT text (alternative text) not only helps improve the accessibility of the webpage but also aids search engines in understanding the content of the images, thus improving the ranking of the images in search results. For example, when selling products, adding an ALT description like "Waterproof Smartwatch, Suitable for Outdoor Sports" can increase the product's visibility in relevant searches.
(3) Use Schema Markup
By adding structured data markup to images and videos, search engines can better recognize and display rich media content, such as showing video previews or product images in search results. This enhanced display format (e.g., rich snippets or video cards) can capture users' attention and improve the click-through rate. For example, adding Product Schema to a product page can display product images directly in search results.
(4) Optimize image file names and formats
Before uploading images, use descriptive file names related to the content, rather than default numbers or meaningless characters. For example, "wireless-bluetooth-earbuds.jpg" is more beneficial for SEO than "IMG_1234.jpg". Also, using modern image formats (such as WebP) can ensure image quality while reducing loading time, thus improving page performance and user experience.
(5)Create eye-catching thumbnails and previews
Thumbnails are an important part of video and article displays. Designing attractive thumbnails can significantly increase the click-through rate. Use bright colors, clear fonts, and relevant image elements to make the thumbnail stand out in search results. For product pages or blog posts, selecting images as feature images can help improve visibility in social media shares and search results.
(6) Use images and videos to attract external links (backlinks)
High-quality original images and videos are more likely to be cited and shared by other websites, bringing external links (backlinks). External links are one of the core factors in search engine rankings, helping to enhance the website's authority and traffic. For example, creating product tutorial videos or infographics can not only increase user engagement but also attract other websites to republish, boosting overall SEO performance.
4、Include Dates or Update Times
(1) Clearly indicate the latest date in the title and description
Including the current year or the latest update date in the title or meta description helps users directly perceive the timeliness of the content. For example, "Best Smartphones of 2025" or "Latest Update: Best Air Purifiers for Home (2025)" lets users know that the content is up-to-date, which can increase the click-through rate.
(2) Update content regularly to keep information fresh
Search engines prefer content that is frequently updated. Regularly checking and updating data, trends, and references in old articles not only improves search rankings but also displays the "Recently Updated" label in search results. For example, product recommendation articles can be updated quarterly to reflect the latest market changes, attracting more user clicks.
(3) Use structured data to mark the update time
By using structured data (Schema Markup) to mark the article’s publish date and update time, search engines can accurately display this information in search results. This approach can improve the credibility of the content, especially for time-sensitive content like product reviews, technical guides, or industry news.
(4) Avoid misleading date updates
While update dates can enhance the content's appeal, simply changing the date without updating the actual content may result in decreased user trust and could even be regarded as low-quality content by search engines. Ensure that every update is accompanied by substantive content changes to maintain good user experience and SEO performance.
(5) Display update information in a prominent position on the page
In addition to marking the date in the title and meta description, you can also prominently note "Last Updated in February 2025" at the beginning or end of the article. This not only enhances the content's transparency but also gives users more confidence to click and read the page content.
(6) Analyze competitors’ date strategies
Regularly check how competitors use dates in similar content to understand their update frequency and ranking changes. If competitors’ content is outdated, you can update your own content and highlight "Latest" in the title to attract more user clicks, thus gaining an advantage in search results.
(7) Update content based on hot topics or seasonality
Updating content based on trending events or seasonal changes can enhance the relevance and appeal of the content. For example, adding specific seasons in "2025 Summer Must-Have Portable Fan Recommendations" or updating review articles based on new product launches can attract more targeted user clicks.
5、Use Clearer and More Descriptive URLs
(1) Use short and meaningful URL structures
Short and intuitive URLs are not only easier for users to understand but also more favorable for search engine crawling. For example, example.com/best-wireless-headphones is more descriptive than example.com/article123?id=456, allowing users to understand the page content before clicking, thus increasing the click-through rate.
(2) Include keywords to enhance relevance
Embedding the core keywords of the page in the URL helps improve the search engine relevance score. For example, a page selling smartwatches could use example.com/smartwatch-features, which not only makes it easier for users to understand but also improves the keyword ranking.
(3) Use hyphens to separate words and avoid underscores
Search engines are better at recognizing phrases separated by hyphens (-), while underscores (_) may be considered as a single word. For example, example.com/bluetooth-speakers is better than example.com/bluetooth_speakers because the former is more SEO-friendly.
(4) Avoid using dynamic parameters and redundant characters
Long dynamic parameters and unnecessary characters make the URL look complicated and unfriendly, decreasing the likelihood of users clicking. For example, avoid using URLs like example.com/product?id=12345&ref=homepage and use example.com/wireless-earbuds instead, so users can easily understand the content at a glance.
(5) Maintain consistent URL naming conventions
Establishing a consistent URL naming convention for all pages on the website helps improve the professionalism and user experience of the site. For example, product pages can uniformly use the format example.com/category/product-name, helping users better navigate and understand the website structure.
(6) Avoid using dates or timestamps to increase the long-term value of URLs
Using dates in URLs might make the content appear outdated, especially for long-lasting pages. Instead of using example.com/2022-smartphone-review, consider using example.com/smartphone-review, which helps maintain the URL unchanged when updating content, preserving long-term SEO effectiveness.
(7) Use lowercase letters to avoid confusion
Use lowercase letters consistently to avoid access errors or search engine crawling issues caused by mixed case in URLs. For example, example.com/SmartWatch-Review and example.com/smartwatch-review may be considered different pages, and the lowercase format is more standardized and uniform.
6、Add Structured Data
(1)What is structured data?
Structured data is a type of code that uses specific formats, such as Schema.org markup, to help search engines better understand the content of a webpage. By adding structured data, search engines can generate rich snippets in search results, such as star ratings, product prices, stock status, and more, increasing the visibility and appeal of the page.
(2) Common types of structured data
- Product: Displays information such as the product's name, price, stock status, etc., suitable for e-commerce websites.
- Review/Rating: Shows user reviews and star ratings, enhancing trust and increasing click-through rates.
- FAQ: Directly displays frequently asked questions and answers in search results, attracting users to click for more information.
- Recipe: Displays detailed information such as cooking time, ingredients, and calories, suitable for food-related websites.
- Event: Lists event times, locations, and ticketing information, helping users quickly access event details.
- Article/BlogPosting: Highlights the author, publication date, reading time, etc., enhancing content authority.
(3) How to add structured data?
Method 1: Write code to add structured data
Using JSON-LD Format: Google recommends using JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) format to embed structured data because it is simple, flexible, and easy to maintain. For example, the code for structured data of product information is as follows:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "无线蓝牙耳机",
"image": "https://example.com/images/earbuds.jpg",
"description": "高品质音效,长续航无线蓝牙耳机。",
"brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "品牌A" },
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "CNY",
"price": "299",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
}
}
</script>Method 2: Use plugins or tools to add structured data
For WordPress websites, you can use plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math, which provide simple interfaces to add structured data without the need to write code.
(4) SEO Advantages of Structured Data
- Increase Click-Through Rate (CTR): Structured data allows webpages to display more detailed information in search results, attracting users to click. For example, product pages with star ratings and prices are often more attractive than plain text links.
- Improve Search Ranking: Although structured data itself is not a direct ranking factor, it can increase page click-through rates and user dwell time, thereby indirectly improving SEO performance.
- Obtain Special Display Positions: Proper structured data can help a webpage achieve priority display positions in search results, such as “Featured Snippets (Featured Snippet)” or “Knowledge Graph (Knowledge Graph)”, increasing brand exposure.
(5) Check and verify structured data
After adding structured data, you can use the Rich Results Test tool to check if the code is correct and ensure that the data can be properly recognized by search engines. Additionally, you can view the structured data report in Google Search Console to see which pages successfully generate rich snippets. If there are any error messages, they should be fixed promptly.
(6) Avoid Over-Optimization and Misuse
Structured data should accurately reflect the content of the page, avoiding false information or abuse of markup (such as adding fake star ratings to products that do not have high ratings). Search engines may penalize such behavior, negatively impacting the overall SEO performance of the site. Ensuring the authenticity and accuracy of data is key to maintaining good rankings over the long term.
(7) Regularly Update Structured Data
Regularly check and update structured data to ensure the information displayed (such as product prices, stock status, event times, etc.) is always up to date. This not only enhances user experience but also prevents a decrease in click-through rate due to outdated information.
7. Improve Page Load Speed
(1) Why is Page Load Speed Important?
Page loading speed not only affects user experience but is also an important factor for search engine rankings. Research shows that if the page load time exceeds 3 seconds, approximately 40% of users will choose to leave. This directly reduces the click-through rate (CTR) and conversion rate, while increasing the bounce rate, which negatively impacts SEO. Search engines like Google have explicitly stated that loading speed is a key part of their ranking algorithms.
(2) Methods to Improve Page Load Speed
Optimize image size and format
- Compress Images: Use tools such as TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or Squoosh to compress images and reduce file size without significantly lowering quality.
- Use Modern Formats: Adopt modern image formats such as WebP or AVIF, which can significantly reduce file size compared to traditional JPEG or PNG.
- Enable Lazy Loading (Lazy Load): Load images only when they appear in the viewport to reduce initial loading time.
Enable browser caching
Set cache headers such as Cache-Control or ETag so that users can load static assets (such as images, CSS, JavaScript) from local cache to speed up page load.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Distribute static resources across global server nodes using CDNs such as Cloudflare, Akamai, or Amazon CloudFront to accelerate load times, especially for cross-region visits.
Minify and combine CSS and JavaScript files
- Minify Code: Remove unnecessary spaces, comments, and line breaks using tools such as UglifyJS or CSSNano to compress files.
- Combine Files: Merge multiple CSS or JS files into one to reduce the number of HTTP requests and improve loading speed.
Reduce HTTP requests and redirects
Each resource bundle (images, CSS, JS) generates an HTTP request. Too many requests will slow down the loading speed. You can effectively reduce the number of requests by merging resources. Try to reduce page redirects (such as 301, 302) to avoid loading delays.
Enable Gzip Compression
Enable Gzip Compression on the server side to reduce data transfer volume and improve loading speed. These compression algorithms can reduce file size by up to 70%.
Optimizing server response time
Choosing a reliable hosting provider with suitable hardware configuration is key to reducing server response latency. Additionally, for dynamic websites, optimizing database queries (such as using Indexes and reducing JOIN operations) can significantly improve load speed.
Using asynchronous loading of JavaScript
Set JavaScript files to async or defer so that the browser can load page content and scripts simultaneously without blocking rendering.
(3) Detect and monitor page loading speed
Using Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights can analyze page loading speed and provide detailed optimization suggestions, including image compression, caching strategies, and script optimization.
Using Lighthouse
Google’s Lighthouse tool (Chrome extension) can generate detailed performance reports, including key metrics such as First Contentful Paint and Time to Interactive.
GTmetrix and Pingdom
These two tools provide global server tests to help evaluate loading speed performance in different regions and provide corresponding improvement suggestions.
(4) SEO benefits of increasing page loading speed
- Improve Search Rankings: Fast-loading websites are favored by search engines, especially on mobile devices. Google's Mobile-First Indexing (Mobile-First Indexing) places particular importance on page speed.
- Reduce Bounce Rate: Websites with fast loading speeds can effectively reduce the chances of users leaving without viewing content, improving user engagement.
- Enhance User Experience: Faster loading speeds mean a smoother browsing experience, increasing user dwell time and conversion rates.
- Increase Click-Through Rate (CTR): Websites with faster loading speeds typically achieve higher click-through rates in search results, as users know these pages can be accessed quickly.
(5) Continuous optimization and maintenance
Page speed optimization is not a one-time task; it requires regular checks and updates. Continuously monitor website performance to ensure that loading speed remains optimal as content grows and technologies evolve. In addition, keep an eye on updates to Google Core Web Vitals to ensure your site consistently meets the latest performance standards.
8、Optimize for Local Search (How to Add Google My Business Info)
(1)Why is local search optimization important?
Local Search Optimization (Local SEO) is especially critical for businesses with physical stores or those targeting customers in specific regions. Studies show that over 46% of Google searches are location-related, and among users conducting local searches, 76% visit a physical store within 24 hours. Therefore, optimizing for local search not only boosts your website’s Click-Through Rate (CTR) but also directly drives offline traffic and sales.
(2) Key local search optimization strategies
Register and complete Google My Business information
- Create an Account: Visit Google My Business to register and verify your business information.
- Complete Your Information: Ensure details such as business name, address, phone number (NAP), business hours, and category are fully filled out.
- Add High-Quality Photos and Videos: Upload clear images of the store's exterior, interior, products, or services to attract potential customers.
- Regularly Update Content: Publish the latest promotions, events, and announcements to stay active and increase the chances of being recommended.
Ensure NAP information consistency
Keep your name, address, and phone number consistent across all platforms (e.g., official website, social media, third-party directory sites). This helps build trust with search engines and improve rankings.
Get customer reviews and responses
- Encourage Customers to Leave Reviews: Actively encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on your Google My Business page.
- Respond to Reviews in a Timely Manner: Whether positive or negative, always respond politely to reviews, showing the business’s professionalism and appreciation for customer feedback. Engaging positively can improve the visibility of the business in local search results.
Use local keywords
Include local keywords such as city names, street names, or regional characteristics in website titles, descriptions, blogs, and meta tags. For example, if you run a coffee shop, you can use keywords such as "Shanghai Jing'an District Hand-Poured Coffee".
Embed Google Maps into your website
Embedding a Google Map on your website’s “Contact Us” page makes it easier for users to find your location and also helps improve your local search rankings.
(3) Other tips to enhance local SEO
Register with local directories and yellow pages sites
Submit your business information to local business directories (such as Dianping, Baidu Maps, and Amap) and industry-related websites to increase exposure and credibility.
Creating localized content
Write content related to the local area, such as local activity guides, community news or regional specialty introductions, to attract local users to search. Such content not only attracts local users, but also improves the weight of search engines.
Setting localized schema markup
Use local business schema markup to help search engines better understand your business information. This allows your business name, ratings, address, and other information to appear directly in search results, increasing click-through rates.
(4) SEO Advantages of Local Search Optimization
- Boost Local Search Ranking: A complete and optimized Google My Business profile allows your business to appear on Google Maps and in the Local Pack (Local Pack), which are more prominent than regular search results.
- Increase Click-Through Rate (CTR): Comprehensive business information and positive reviews attract more users to click, driving online traffic.
- Increase Actual Store Visits: Local search users typically have a clear purchase intent. Local SEO can effectively convert online traffic into offline customers.
- Enhance Brand Reputation: Consistent and detailed local information, positive user reviews, and timely interactive feedback help boost brand image and user trust.
(5) Continuously monitor and optimize local search
Local SEO is an ongoing process that requires regular review and update of Google My Business information, monitoring of review feedback, and adjusting content based on user needs. At the same time, use tools such as Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track local search traffic and user behavior in order to continuously optimize strategies and maintain competitive advantage.
Conclusion: “From the Underlying Logic of Google SEO Traffic to Best Technical Practices” is a ten-chapter guide with over 70,000 words, systematically explaining the core theories and practical skills of SEO. It aims to help readers comprehensively understand SEO traffic strategies and optimization techniques. These practices are not only actionable but also aligned with the latest changes in search engine algorithms, empowering businesses and individuals to stand out in a competitive market. Whether you're new to SEO or an experienced professional, you’ll find practical methods and deep insights in this technical tutorial. In addition, Logic Digital Technology also provides professional SEO Optimization services. If needed, feel free to contact the Marketing Director at Logic Digital Technology for more expert SEO advice.
Logic Digital Technology (SZLOGIC) All rights reserved. This article is welcome to be shared by individuals to help newcomers entering the cross-border e-commerce independent website track, but reproduction for commercial purposes is prohibited.